
Protecting Our Homeland: NNSA successfully secured communities against radiological threat and “dirty bombs.”
Fostering the next generation of nuclear security and nonproliferation leaders, NNSA has renewed a $25 million grant for another 5 years to an R&D consortium led by the University of California, Berkeley that directly supports our vital missions.

NNSA just checked Oklahoma off the list of states cleared of cesium irradiators. This is a major milestone in enhancing security across the nation. Read more about how NNSA worked to eliminate the radiological risk these devices pose.
Department of Energy gives OK for Philippines and Singapore to get U.S. exports of nuclear technology and assistance.

NNSA and Japan’s Kyoto University converted two cores from the Kyoto University Critical Assembly from using highly enriched uranium to high-assay low-enriched uranium fuel. It's a nonproliferation and HALEU research milestone.

NNSA and Texas A&M University have teamed up to combat the New World Screwworm and protect America’s farms and ranches. The partnership advances eBeam technology and radiological security while safeguarding agribusiness nationwide.

NNSA just removed the last cesium irradiators from Kansas, a major advancement in eliminating radiological risk across the nation. To enhance national security, we helped them replace these devices with more secure technology.

NNSA and Department of Health and Human Services’ Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services work together to support manufacturing Mo-99, a key diagnostic tool for doctors that is administered in the U.S. 40,000 times a day.

From San Francisco to Indianapolis to New York to tiny Vinton, Louisiana, the RadSecure 100 Initiative gave communities a security upgrade.
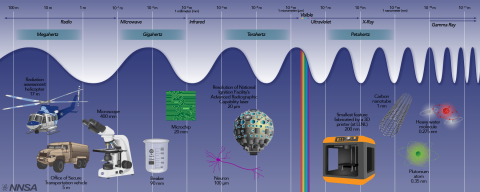
At NNSA’s labs, plants, and sites, research supporting our vital missions reaches across the electromagnetic spectrum – from radio waves to gamma rays. Sometimes that innovation spills into other areas, too, enabling tomorrow’s technological wonders.

