RSS
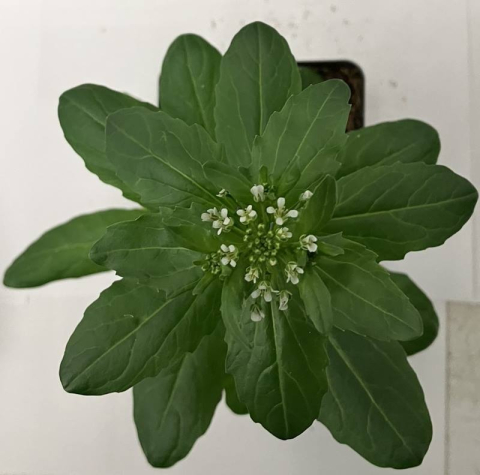





Scientists engineered camelina and pennycress seeds to produce nearly pure specialized oils, paving the way for improved biofuel production.

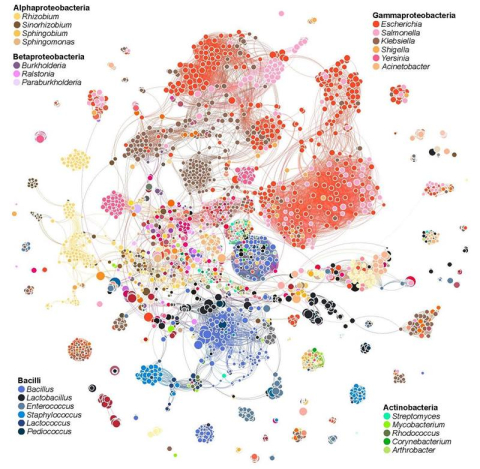
Analysis of bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems sheds new light on how microbes interact with other members of their communities.

Quantum ghost imaging of live plants at light levels lower than starlight gives new perspectives on plant processes.

Nutrients related to vitamin B12 influence microbial growth and reshape soil microbiomes.

Scientists use gene editing to create a yellow-seeded camelina that may boost oil yield.

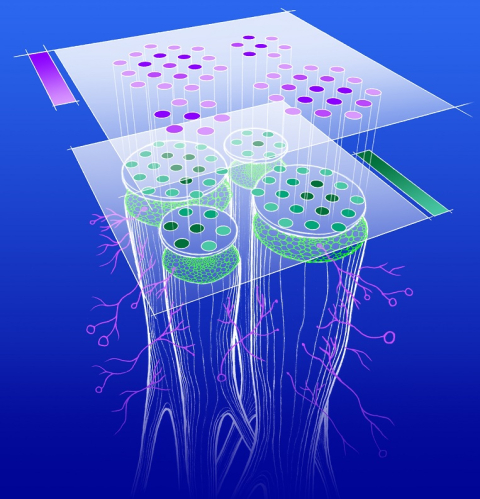
Spatial transcriptomics, combined with single-cell expression profiling, reveals new information on plant/arbuscular mycorrhizal interactions.

Leveraging a new genome annotation tool, researchers identified ‘talented’ microorganisms with genes for transforming polyphenols in peatlands.

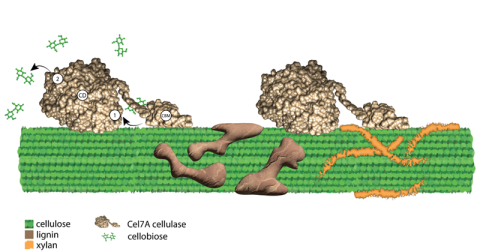
A specialized microscope allows investigations of single molecules of cellulase enzymes.

Genetically modified bacteria brews two valuable products from underutilized plant fiber, potentially reducing fossil fuel use.

Scientists create a genome-wide map of gene activity in bacteriophages.

