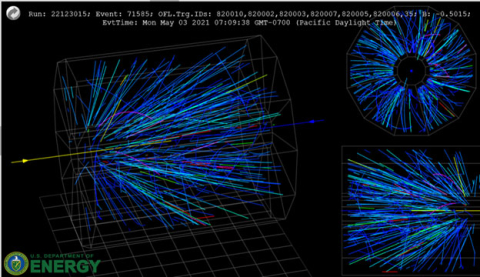
Colliding gold nuclei at various energies enables scientists to investigate phases of nuclear matter and their possible co-existence at a critical point.

A first-of-its-kind measurement of the rare calcium-48 nucleus found a neutron-rich “thin skin” around a core of more evenly distributed protons and neutrons.
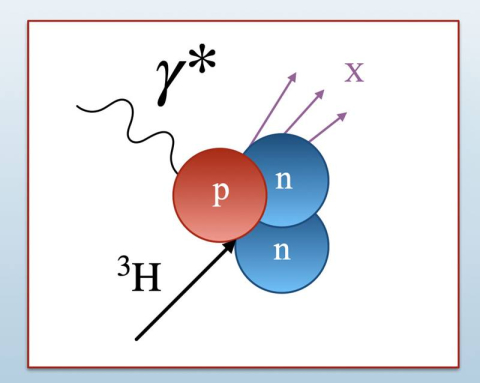
Nuclear physicists find that the internal structures of protons and neutrons may be altered in different ways inside nuclei.

Predictions for future measurements at the Electron-Ion Collider may help solve ‘proton spin’ mystery.
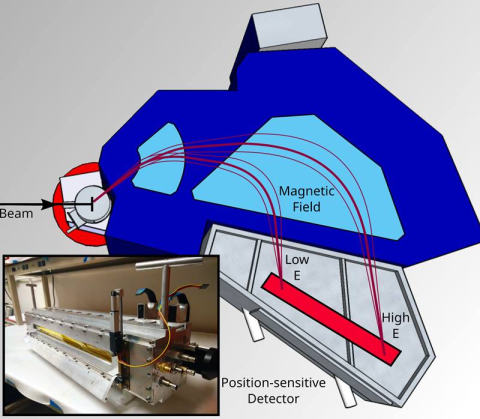
The energy of a key resonance in sodium destruction is found, affecting our understanding of globular cluster evolution.
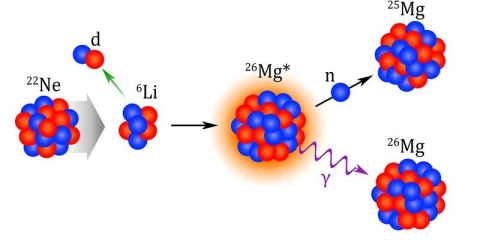
A key reaction in the slow neutron-capture process that forms elements occurs less frequently than previously thought.

Scientists explore the origin of Aluminum-26 in stars with a nuclear reaction that exploits the fact that neutrons and protons are stunningly similar.

A new machine learning system diagnoses particle accelerator component issues in real-time.
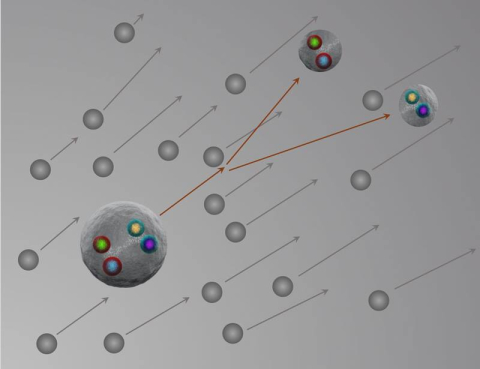
Scientists start studying the structure of exotic hadrons by looking how they interact with nearby particles.
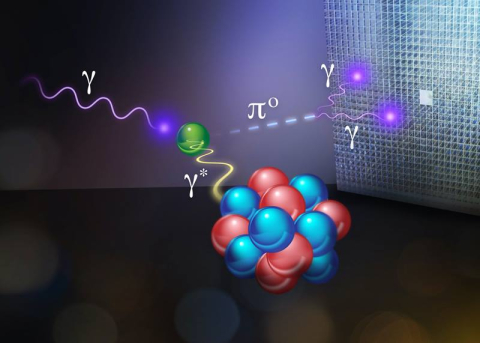
A result 20 years in the making: Most precise measurement yet of the lifetime of the charge-neutral pion that keeps protons and neutrons together.

