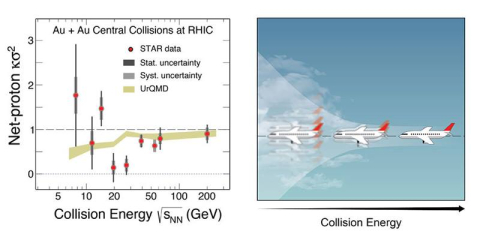
Fluctuations in data from collisions of gold nuclei hint at a possible ‘critical point’ in how nuclei melt.
The types of ancient stellar explosions that gave rise to meteoric presolar grains can now be identified thanks to observations of gamma rays emitted by the argon-34 isotope.
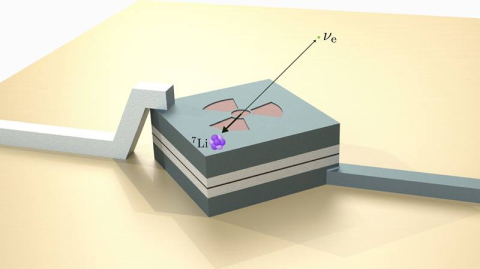
new approach for measuring nuclear recoils in superconducting quantum sensors enables the first limits on sterile neutrinos from beryllium-7 decay.

Nuclear theorists put pen to paper and code to computer to detail this subatomic particle’s inner structure.

Scientists conduct the first direct probes of the interactions between protons and neutrons inside nuclei.
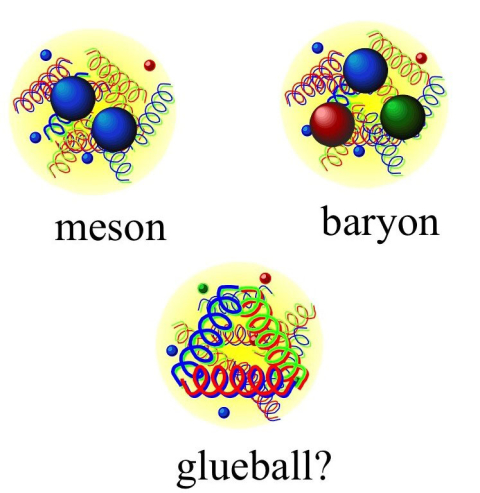
ists predict that gluons, the particles that bind quarks, also bind to one another, but they have never unambiguously observed globs of pure ‘glue.’
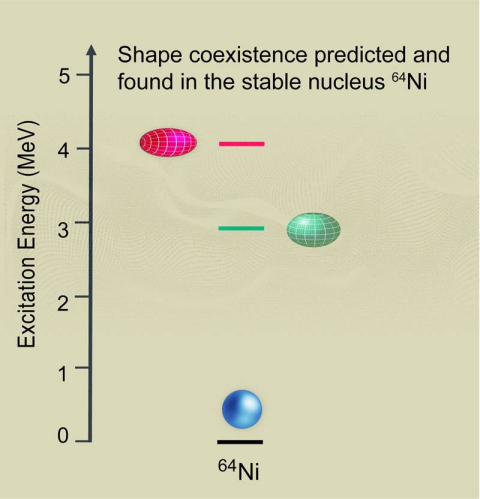
Scientists track down coexistence of multiple shapes in the Nickel-64 nucleus: a spherical ground state and elongated and flattened shapes.
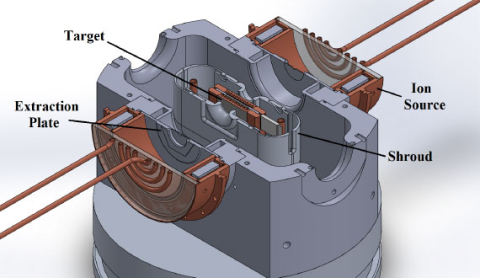
New measurements provide insights for geochronology and reactor design.

Nuclear physicists narrow the search for a rare nuclear decay that can explain the origin of matter in the universe.

Built with detector technologies used in nuclear physics experiments, the system monitors radiation treatments in hard-to-reach areas.

