
On the heels of the Summer Olympics, two Hanford Site contractors have finished a first-time relay of test glass while preparing for a giant leap forward in the cleanup mission.
Thanks to a new training tool, workers at the Hanford Site are getting hands-on experience operating cranes, just on a smaller scale.

Contractors at the Hanford Site recently led a site cleanup tour for up-and-coming community leaders who are part of the latest Leadership Tri-Cities (LTC) class.
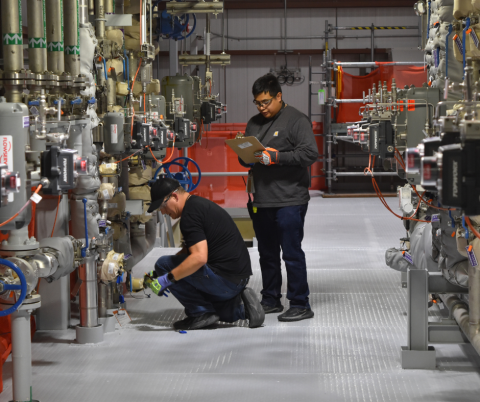

Contractor teams recently collaborated to transfer 4,000 gallons of wastewater between two Hanford Site facilities.
Hanford Site wildlife biologists take great care in protecting migratory birds. The environmental team with U.S. Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management contractor Hanford Mission Integration Solutions conducts bird nest surveys prior to any work activities on the ground.
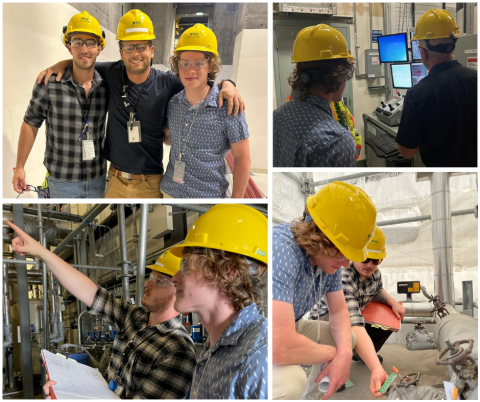

A partnership between the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant and Oregon State University recently provided an engineering student with a unique opportunity.

Workers at the Hanford Site recently finished filling the last large concrete basin at the K Reactor Area with cement-like grout. The basin stored reactor fuel rods from the plutonium production mission.

A One Hanford contractor partnership has developed a new process to ensure radioactive and chemical tank waste is ready for pretreatment quickly and efficiently at the Hanford Site.
Risk reduction is a key component of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management (EM) cleanup mission at the Hanford Site. Placing the K East Reactor into interim safe storage, also known as “cocooning,” in October 2022 marked a significant accomplishment in that mission.
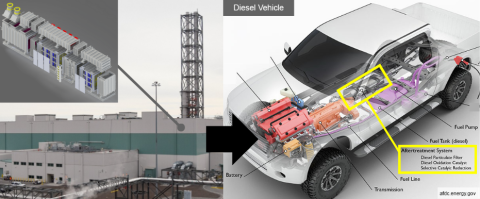
Crews at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant are maintaining a large-scale thermal catalytic oxidizer to prepare for operations.

