What are Dual-Use Photovoltaic Technologies?
Dual-use photovoltaic (PV) technologies, also known as dual-use PV, are a type of PV application where the PV panels serve an additional function besides the generation of electricity. While the most prominent dual-use application is building-integrated PV (BIPV), other dual-use PV technologies include agrivoltaics, floating photovoltaics (FPV), and vehicle-integrated photovoltaics (VIPV).
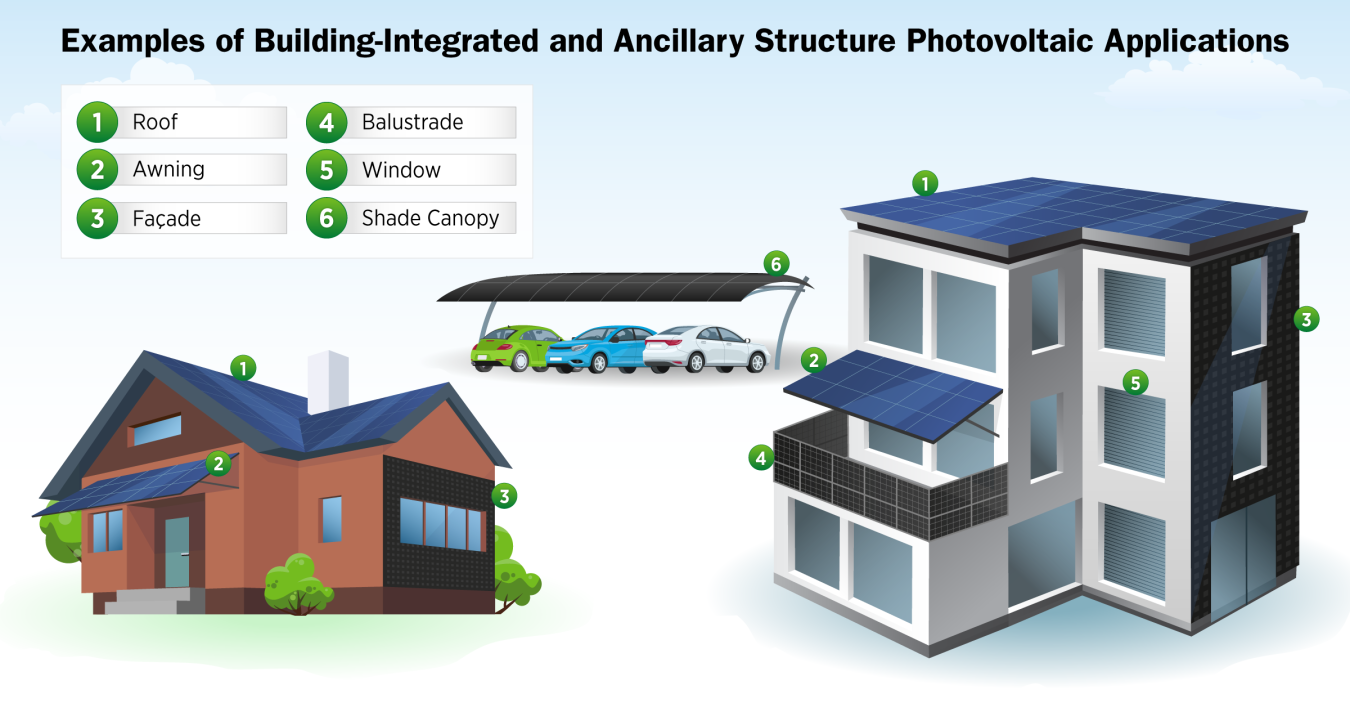
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
In BIPV, solar materials are used to replace conventional building materials in parts of the building’s structure like the roof, skylights, balustrades, awnings, and facades. The most commonly recognized type of BIPV is carports and parking shade structures. BIPV serves as the outer layer of a building, and it generates electricity for on-site use or exports it to the grid. This differs from traditional rooftop solar, where PV modules are placed on top of an existing roof.
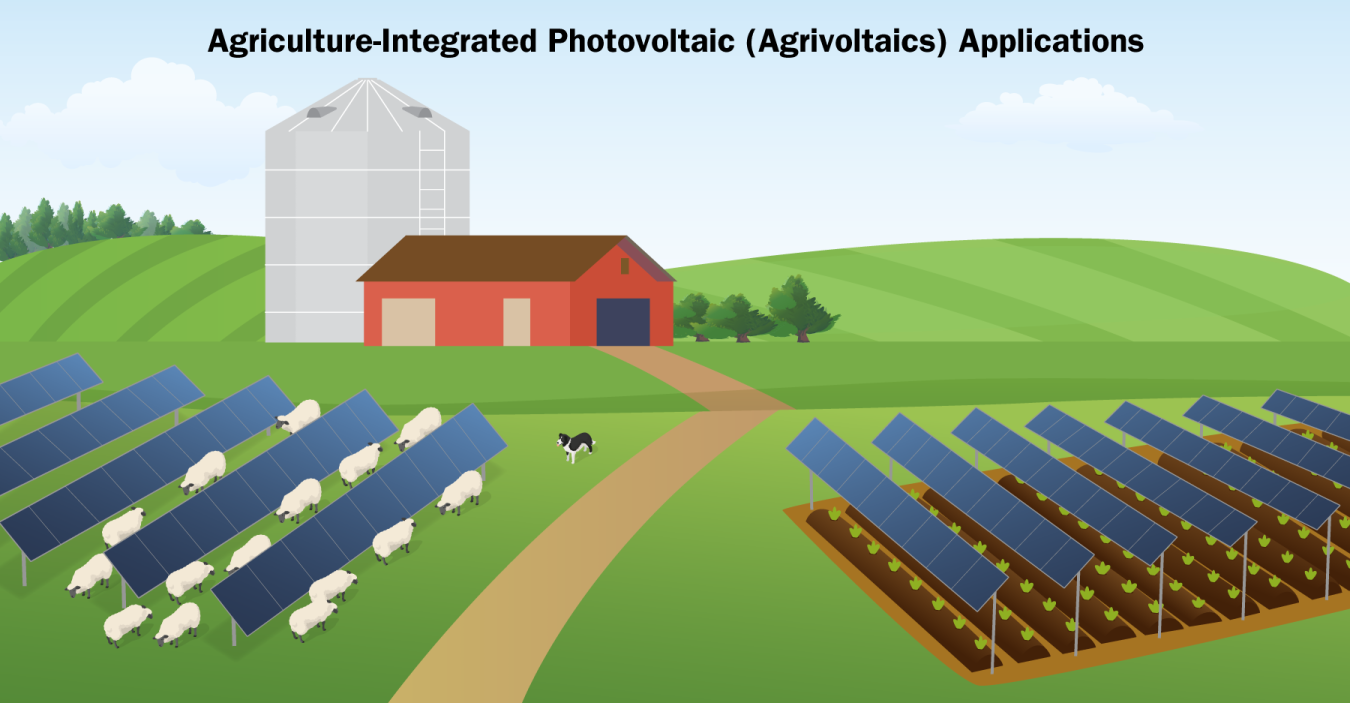
Agrivoltaics
Solar and agriculture co-location, also referred to as agrivoltaics, is defined as agricultural production, such as crop or livestock production or pollinator habitats, underneath or between rows of solar panels. In addition to solar energy production, the PV panels can also provide shade and potentially reduce the need for irrigation of the site on which they are located. Most large, ground‐mounted solar PV systems are installed on land used only for solar energy production, making agrivoltaics unique in that it can provide benefits to both the solar and agricultural industries. Learn more about agrivoltaics.
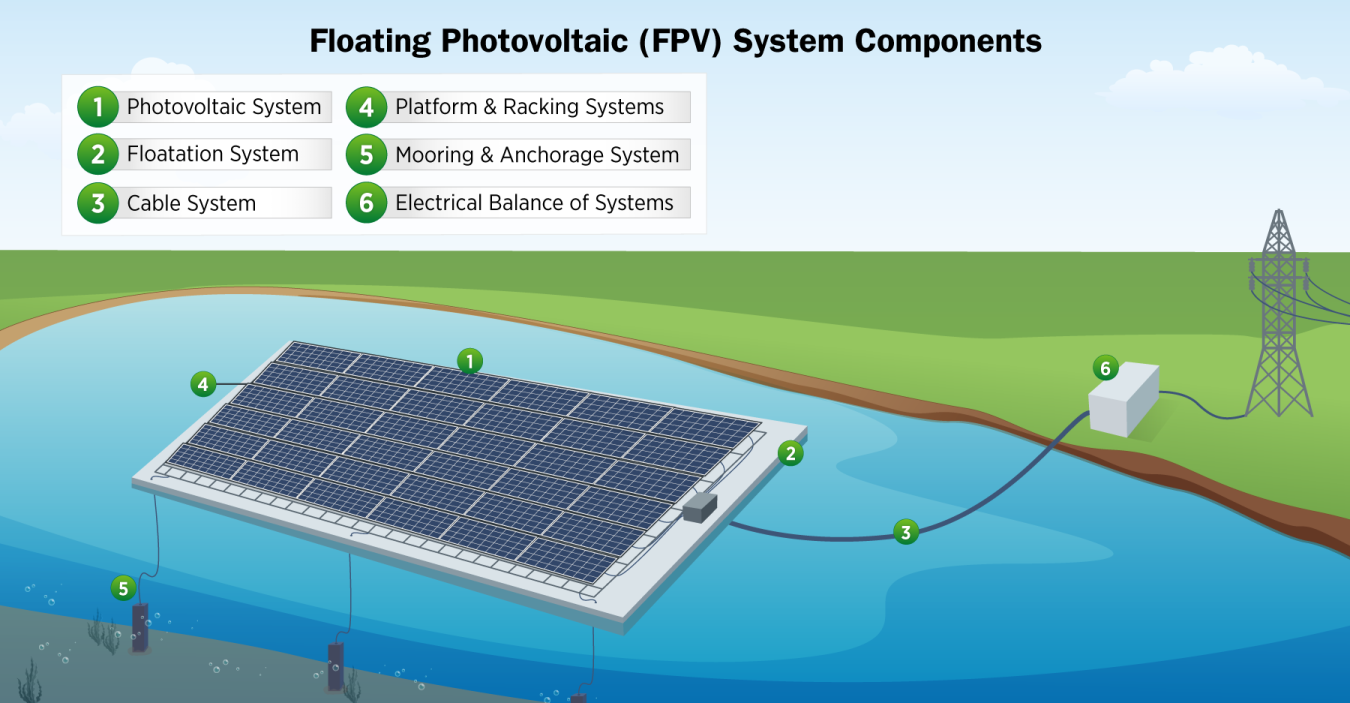
Floating Photovoltaics (FPV)
FPV, also known as floatovoltaics, mounts solar panels on floating structures that are deployed on reservoirs, lakes, and other large man-made bodies of water as well as in near-shore and off-shore marine applications. When deployed on bodies of water, FPV systems can reduce evaporation and leverage otherwise unused space, reducing land-use concerns.
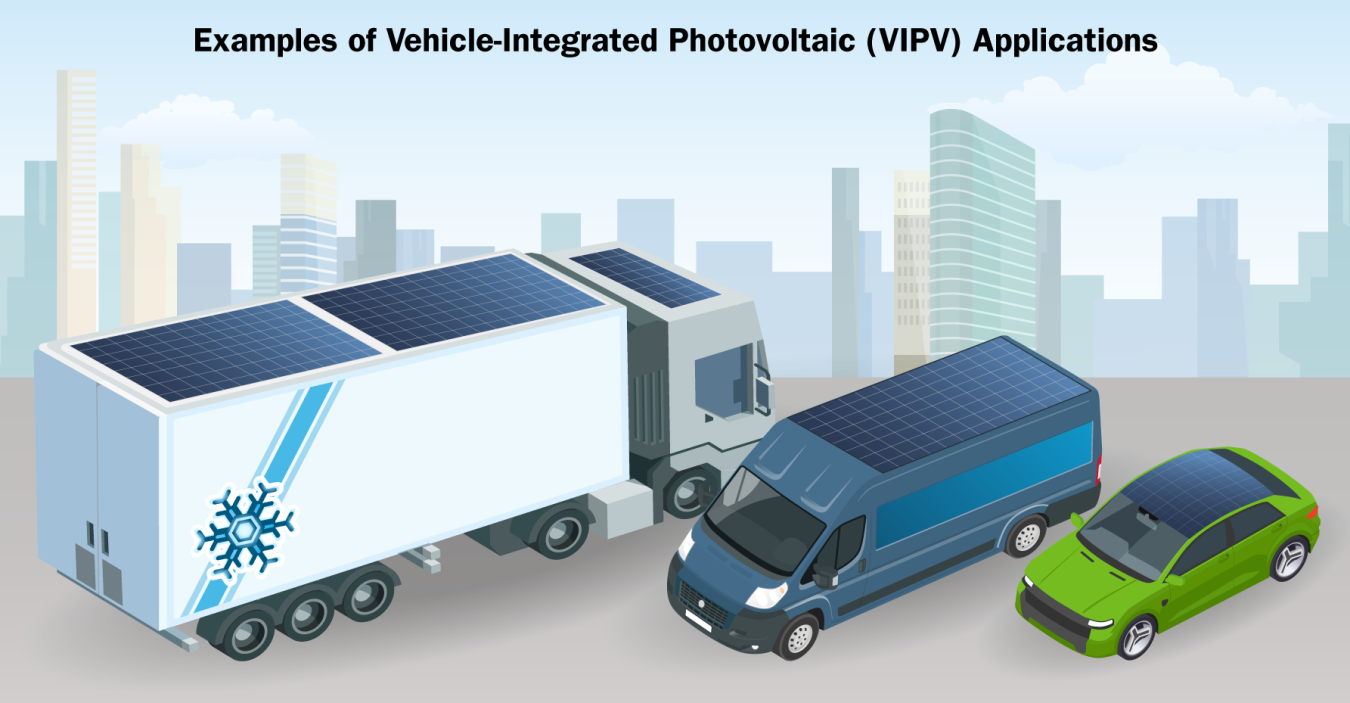
Vehicle-Integrated Photovoltaics (VIPV)
With VIPV, solar cells are mechanically and electrically added into the design of a vehicle. The PV elements integrate into the vehicle exterior and the electric system to supply power to on-board electronics or batteries while also serving as the vehicle’s roof, hood, door, or fender providing structural and safety functionality.
While not technically dual-use, another type of vehicle photovoltaics—vehicle-added or attached PV (VAPV)—attaches traditional PV modules to the existing vehicle structure to generate energy.
If commercialized, VIPV and VAPV offer two main uses: propulsion in electric vehicles, which improves the range of the electric vehicle; and power for systems such as heating and cooling.
Why are Dual-Use Photovoltaic Technologies Important?
Innovative dual-use technology like agrivoltaics, BIPV, FPV, and VIPV creates opportunities to develop domestically made products capable of expanding PV markets as well as reducing reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
By integrating solar energy systems into existing landscapes, dual-use PV and has the potential to minimize land-use concerns and creates opportunities for more aesthetically pleasing solar energy systems.
Research in dual-use PV technologies supports the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Solar Energy Technologies Office’s (SETO) goals of improving the affordability, performance, and value of solar technologies and establishing a domestic manufacturing base. Learn more about SETO’s PV goals.
SETO Research in Dual-Use Photovoltaic Technologies
SETO research in these technologies ultimately aims to support U.S. solar manufacturing, spur innovation, reduce the soft costs and other barriers to equitable solar energy deployment. Specifically:
- BIPV research projects are developing aesthetically pleasing, high-efficiency BIPV products that reduce costs for homeowners and building professionals.
- FPV projects are improving U.S. competitiveness in the floating solar market and optimizing the economic and environmental value of FPV.
- Vehicle PV projects are generating technological advancements to lower the cost of solar power generation systems and installation on vehicles.
SETO funded the following projects related to dual-use PV technologies:
2022
- Gismo Power’s Wheeling Gismo Power onto Residential Driveways Enables Cost-Effective Solar Energy for Lower to Middle Income Homes – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY22 Phase 1
2020
- The Architectural Solar Association’s Architectural Solar Education for Design and Construction Professionals – Buildings Energy Efficiency Frontiers & Innovation Technologies (BENEFIT) – 2020
- Gismo Power’s Portable Solar Carport with Integrated EV Charger – American-Made Solar Prize Round 5
- Toledo Solar’s Low-Cost Manufacturing of Semitransparent CdTe PV for Building Integration – Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2020 Funding Program (SETO 2020) Innovations in Manufacturing – Hardware Incubator
2019
- Nanoflex Power Corporation’s Advanced Manufacturing of Low-Cost Building Integrated Organic Photovoltaic Modules – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY19 Phase 1
2018
- University of Michigan’s Semi-Transparent, Reliable and Efficient Scalable Organic Solar Cells for Building Integrated Applications – Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2018 Funding Program (SETO FY2018) Photovoltaics
2022
- Noria Energy's Autonomous Cable-Free Anchoring for Floating Solar - American-Made Solar Prize Round 6
- Dissigno International’s Platform for Floating Solar-Powered Water Technologies - Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY22 Phase 2
- Idaho National Laboratory’s AquaPV: Foundational Analysis and Industry Guidance on Floating PV for Reservoirs and Estuaries - Solar Energy Technologies Office Lab Call FY2022-24 – Soft Costs
2021
- AccuSolar’s U.S. Floating Solar Manufacturing Innovations for Improved Cost and Performance – Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2021 Systems Integration and Hardware Incubator Funding Program
- Dissigno International’s Solar Float Designed to Leverage U.S. Contract Manufacturing – Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2021 Photovoltaics and Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power Funding Program
- RCAM Technologies’ Bio-inspired 3D Concrete Printed Anchors for Floating PV – American-Made Solar Prize Round 5 - Hardware Track
- Dissigno International’s DC Bus Platform for Floating Solar-Powered Aeration – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY21 Phase 1
- Floating Island International’s Advancing the Development of Floating Solar-Powered Nanobubble Aeration Systems for Use with Floating Treatment Wetlands in Natural and Man-Made Waterbodies – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY21 Phase 1
- Epsilon Innovation Group’s Floating Solar Powered Aeration System for Aquaculture – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY21 Phase 1
- Hawaii Fish Company’s Floating Solar Aquaculture Aerator with Secondary Renewable Energy Option – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY21 Phase 1
- FarmAfield Labs’ Adding Value to Floating Aeration Systems via Solar-Powered Destratification Equipment – Solar Topics in Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) – FY21 Phase 1
2018
- University of Central Florida’s Quantifying and Valuing Fundamental Characteristics and Benefits of Floating Photovoltaic (FPV) Systems – Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2018 Funding Program (SETO FY2018)
2022
- PI Energy’s Ultra-Thin Flexible Solar PV, for More Surfaces – American-Made Solar Prize Round 6
Additional Resources
- Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics
- Quarterly Solar Industry Update
- PV Innovation Roadmap
- Vehicle Photovoltaics Request for Information and RFI Summary Report
- BIPV Request for Information and RFI Summary Report
- BIPV Market Research Study (PDF)
- Agrivoltaics Market Research Study (PDF)
- FPV Market Research Study (PDF)
- PVinMotion 2023 Presentation (PDF)
- RE+ 2022 Workshop – Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Beyond the Shingle (PDF)
- GreenBuild 2022 Workshop – Building-Integrated Photovoltaics: Beyond the Shingle (PDF)
- Buildings XV Workshop - Current Challenges, Opportunities, and Research Needs of Building-Integrated PV Systems (PDF)
Learn more about PV research, manufacturing & competitiveness research, soft costs research, other solar energy research in SETO, and current and former funding programs.

