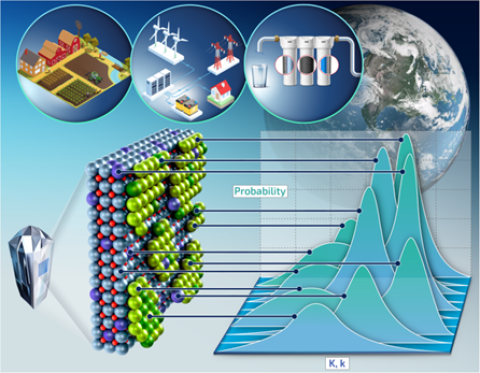
Researchers propose a new approach to modeling adsorption processes that affect how pollutants move through soil, water, and rock.

Automatic speech recognition predicts earthquake fault displacement.
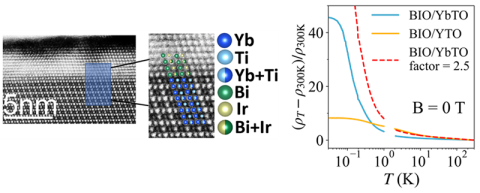
The spin fluctuations of an insulating quantum magnet determine how electricity flows in a nearby metal film.
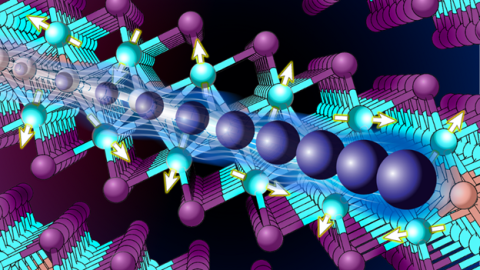
The 2D material cerium silicon iodide contains the same heavy electrons responsible for heavy fermion physics, something so far seen only in 3D materials.
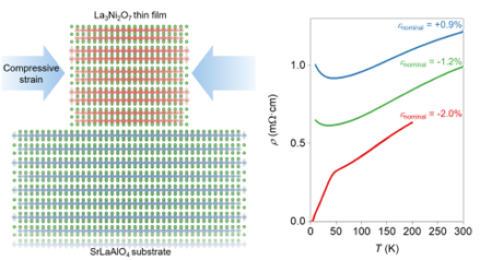
Researchers have learned how to retain superconductivity at ambient pressure in a new class of high temperature superconductors.
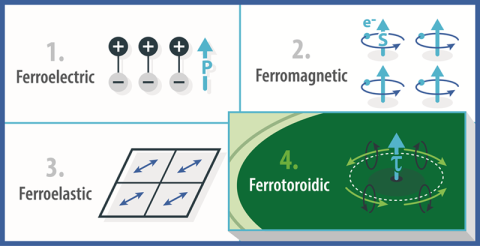
Mapping a way to ferrotoroidicity: the long-sought fourth ferroic order with magnetic-electric properties that can enable new technologies.
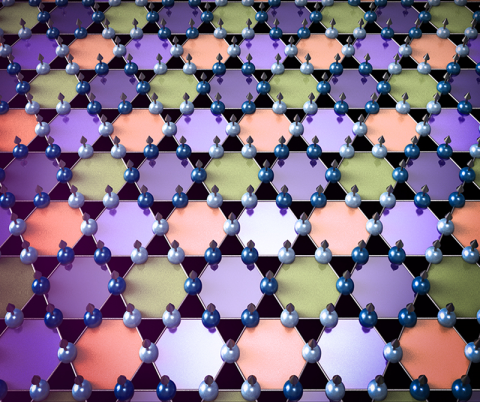
An unexpected electron behavior called charge density waves in an iron-germanium metal material presents a new paradigm in emergent quantum phenomena.
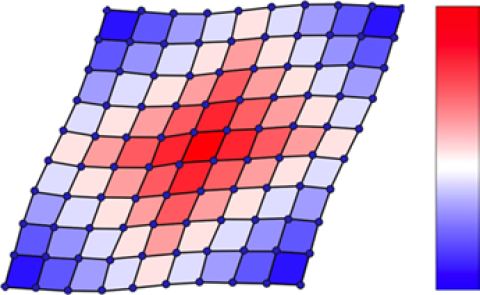
A “neutron camera” device reveals how a thermoelectric material maintains an overall crystalline structure despite local dynamic disorder
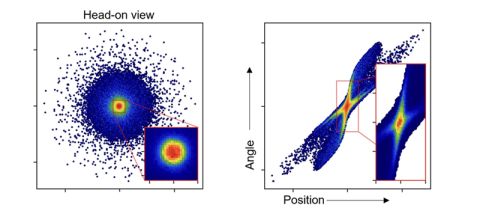
The intra-beam repulsion that typically degrades electron beam quality can now be used to improve it
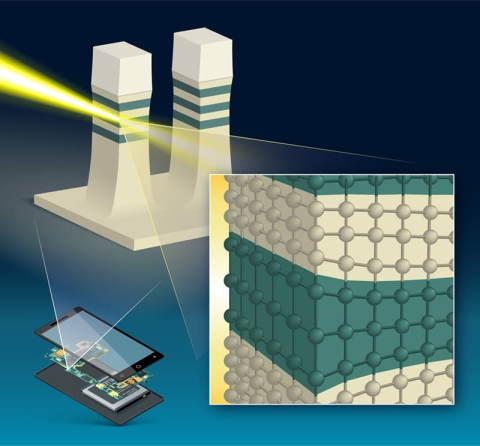
Scientists found two competing mechanisms that contribute to the deformation of nanosheet materials used in cutting-edge computer components.

