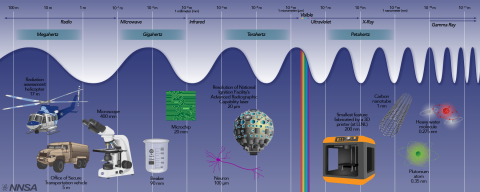
At NNSA’s labs, plants, and sites, research supporting our vital missions reaches across the electromagnetic spectrum – from radio waves to gamma rays. Sometimes that innovation spills into other areas, too, enabling tomorrow’s technological wonders.

The entire rainbow of radiation that the human eye can see makes up just 0.0035 percent of the spectrum. At NNSA it helps us ensure that we’re working with pure materials, watch for missile launches, and create flat lenses.

The achievement significantly enhances radiological security and underscores NNSA's commitment to keeping America safe from radiological terrorism.
In January 2025, NNSA Administrator Jill Hruby posted the following as a letter in Science, in response to the June 2024 article titled “The weapons potential of high-assay low-enriched uranium.”

The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration and the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs co-hosted the seventh Nuclear Security Working Group this month at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.

The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration and Japan’s Kyoto University have converted the Kyoto University Critical Assembly “Core C” from highly enriched uranium to high-assay low enriched uranium fuel.
Meet Ed McLean. His family lawyer and his father influenced him deeply and positively. His service in the U.S. Air Force prepared him to help NNSA's Office of Global Material Security improve its processes and run more efficiently.

Senior leaders from around the U.S. government attended the 68th International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) General Conference (GC) September 16-20 in Vienna, Austria, to advance nuclear energy, safety, security, safeguards, emergency preparedness and response, peaceful uses, nonproliferation, and other nuclear-related issues.

In September, NNSA’s Office of Radiological Security hosted a conference in Thessaloniki, Greece, highlighting the medical efficacy of alternative technologies – like X-ray – to high-activity radiological sources and their ability to reduce the risk of terrorism.
NNSA has released Prevent, Counter, and Respond—NNSA’s Plan to Reduce Global Nuclear Threats (NPCR) FY 2025-2029. This report highlights pressing nuclear and radiological challenges at home and abroad.

