A2e initiative addresses the need to have reliable, applicable wind data by establishing and funding the Data Archive and Portal (DAP).
Wind Energy Technologies Office
October 21, 2019Wealth of Atmosphere to Electrons data informs wind industry decisions
More than 6% of electrical power in the United States comes from wind plants. As a variable energy resource, wind power requires accurate forecasts to integrate with the electrical system efficiently and ensure grid reliability.
This article is part of the
Existing forecast models have advanced in recent years, but they often still exhibit errors that can create losses for generators and challenge grid stability. To improve the accuracy and reduce the uncertainty of the models, researchers involved in the DOE Atmosphere to Electrons (A2e) initiative are conducting data-intensive numerical and field studies.
A2e research focuses on optimizing electrical power production of wind plants, while lowering the associated risk and cost. As part of this program, WETO established the Data Archive and Portal (DAP), managed by DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). The DAP gives users easy and secure access to validated laboratory data, field and benchmark model data, and offshore data from A2e research activities.
“This ultimately results in improved model accuracy and more reliable intelligence for decision making related to wind power research and development,” said Will Shaw, PNNL wind energy program manager.
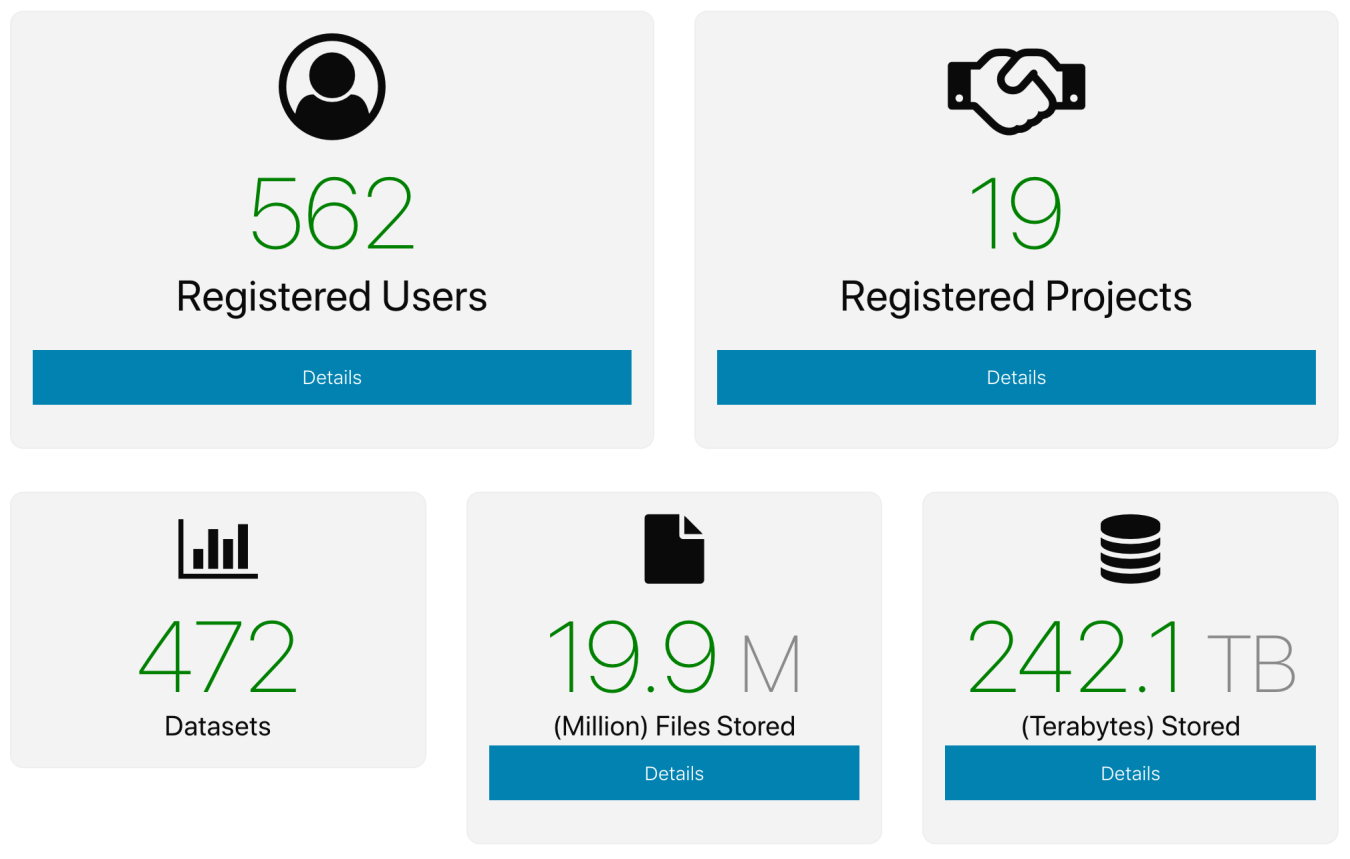
Data collected in the DAP provides researchers, wind technology manufacturers, wind plant operators, and industry consultants with information needed to make decisions about factors such as location, wind collection optimization, and evaluation of the impacts of wake effects of sites. Since its inception, more than 550 users have accessed the DAP’s 472 data sets, including 19.9 million files and more than 242.1 terabytes of historical field studies dating back to 2000.

The Data Archive and Portal is part of the A2e initiative, which focuses on optimizing electrical power production of wind plants. Illustration by NREL
Researchers are able to access data related to instruments like sodar, radar, and lidar used at wind power plants and review measurements involving pressure, wind direction, speed, temperature, and turbulence. Over the next five years, researchers plan to collect and monitor DAP data for a field study off the coast of Maine in preparation for developing advanced offshore wind technology.
The DAP collects, stores, and disseminates A2e data using state-of-the-art technology through the secure cloud-services platform from Amazon Web Services and PNNL’s research-computing resources. The standardized data sets can be accessed by the scientific community for instant validation and easy analysis, allowing users to reduce individual requirements for storage and operational tools.
The DAP provides users-ranging from researchers to wind power plant operators-with historical studies and model output. Figure from PNNL
Data from the DAP framework feed not only WETO research, but projects for other offices and agencies as well. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) used DAP meteorological data as the basis for its High-Resolution Rapid Refresh model, facilitating improvements to National Weather Service operational forecast models. These modifications have already yielded quantitative improvements in short-term operational forecasts, with more than 200 terabytes of model output produced by NOAA stored on the DAP. The DAP framework is also being used to build similar platforms for the Energy Department’s EERE Vehicle Technologies Office, such as Livewire Data Platform.
The DAP’s secure data management capabilities are increasing the willingness of the wind industry to share its proprietary data while maximizing access to large field data sets—all of which has the potential to accelerate time to market and reduce costs for new wind technologies. Register to access the DAP.
-
System operators have a new tool for bringing intuition to the deluge of wind data—a visualizer for wind power forecasts called WindView.
-
 Offshore wind representatives met this spring to discuss meteorology and oceanography research to support offshore wind projects in the U.S.
Offshore wind representatives met this spring to discuss meteorology and oceanography research to support offshore wind projects in the U.S. -
 With a host of new partners and an open call for research proposals, the $41-million National Offshore Wind R&D Consortium is ready to make a splash.
With a host of new partners and an open call for research proposals, the $41-million National Offshore Wind R&D Consortium is ready to make a splash. -
 Researchers are analyzing alternative blade concepts that could almost double the size of today’s blades.
Researchers are analyzing alternative blade concepts that could almost double the size of today’s blades. -
 A new scalable offshore floating wind system provides novel solutions to cut costs and overcome challenges of deepwater offshore environments.
A new scalable offshore floating wind system provides novel solutions to cut costs and overcome challenges of deepwater offshore environments.
Explore previous editions of the Wind R&D Newsletter or browse articles by topic:

