
To support ecologically responsible solar deployment, Argonne National Laboratory developed a camera powered by artificial intelligence to see how birds interact with solar panels.

Sunvapor designed a solar collector to cut costs and optimize the supply chain by using less energy to manufacture the structural components.

The NRECA ACCESS project researched how to make solar energy affordable for low-and moderate-income (LMI) communities. Through this project, a toolkit was developed to assist electric co-ops and the broader industry deploy equitable solar projects.
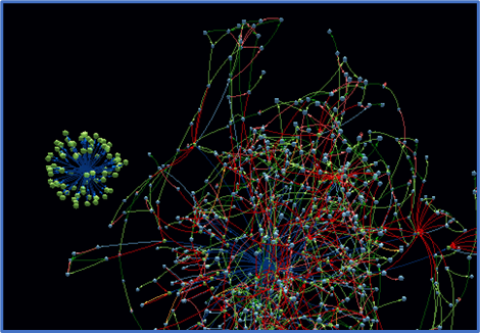
The @DisCo software helps utilities and solar manufacturers prevent cybersecurity and ransomware attacks affecting the U.S. electric grid. The software identifies cybersecurity vulnerabilities in the firmware of devices like solar inverters.

The U.S. Department of Energy funded the Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC) to address standalone energy storage and solar-plus-storage interconnection challenges on the distribution grid.

Microgrids are small electric grids that can operate while disconnected from the main grid. Learn how a new tool that networks multiple microgrids with solar-plus-storage together can lead to community resilience.

With funding from SETO, the North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center developed a policy guide for cooperative and municipal utilities in the Southeast to help them make community solar more available to customers.

Siting solar arrays is a challenge shared by developers, state and local governments, and communities. With the help of Energy Department funding, Nevados developed hardware that opens new sites by enabling solar panel installation on uneven terrain.
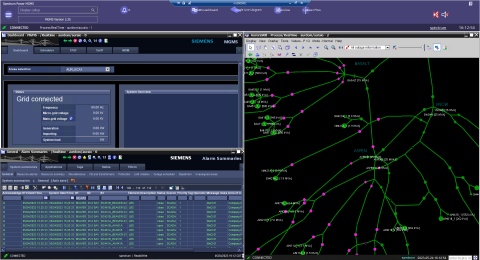
With a $5 million award from SETO, Siemens develop a three-layer energy management system for microgrids that helps secure both microgrids and the larger electric grid against physical threats and cyberattacks.
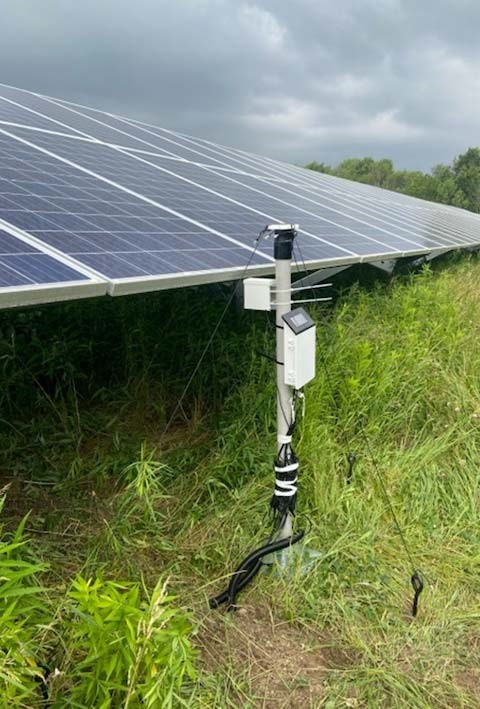

Communities can now use a solar-specific tool to understand stormwater runoff at their local solar energy installations.

