Note: This page was updated in May 2019 with the most recent manufacturing energy Sankey diagrams (using the latest U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) Manufacturing Energy Consumption Survey (MECS) data for 2014 and updated assumptions). The earlier version of the Sankey diagrams, based on 2010 EIA MECS data, are still available here: 2010 EIA MECS data Sankey diagrams.
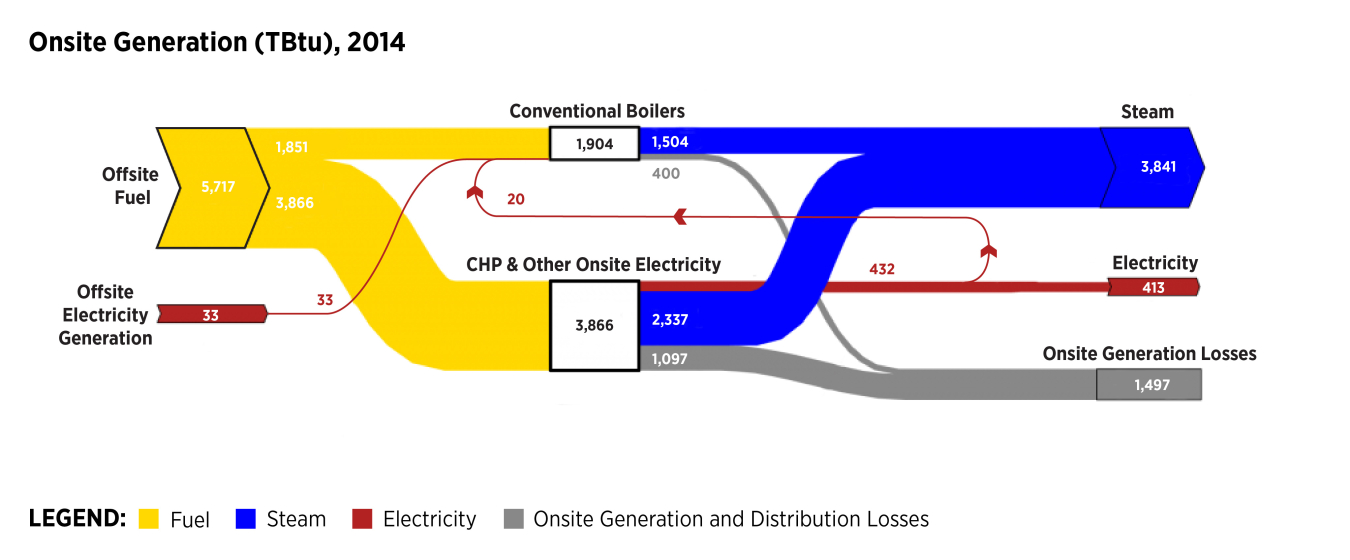
The Onsite Generation Static Sankey diagram shows how steam and electricity are generated by U.S. manufacturing plants, based on EIA MECS data for 2014.
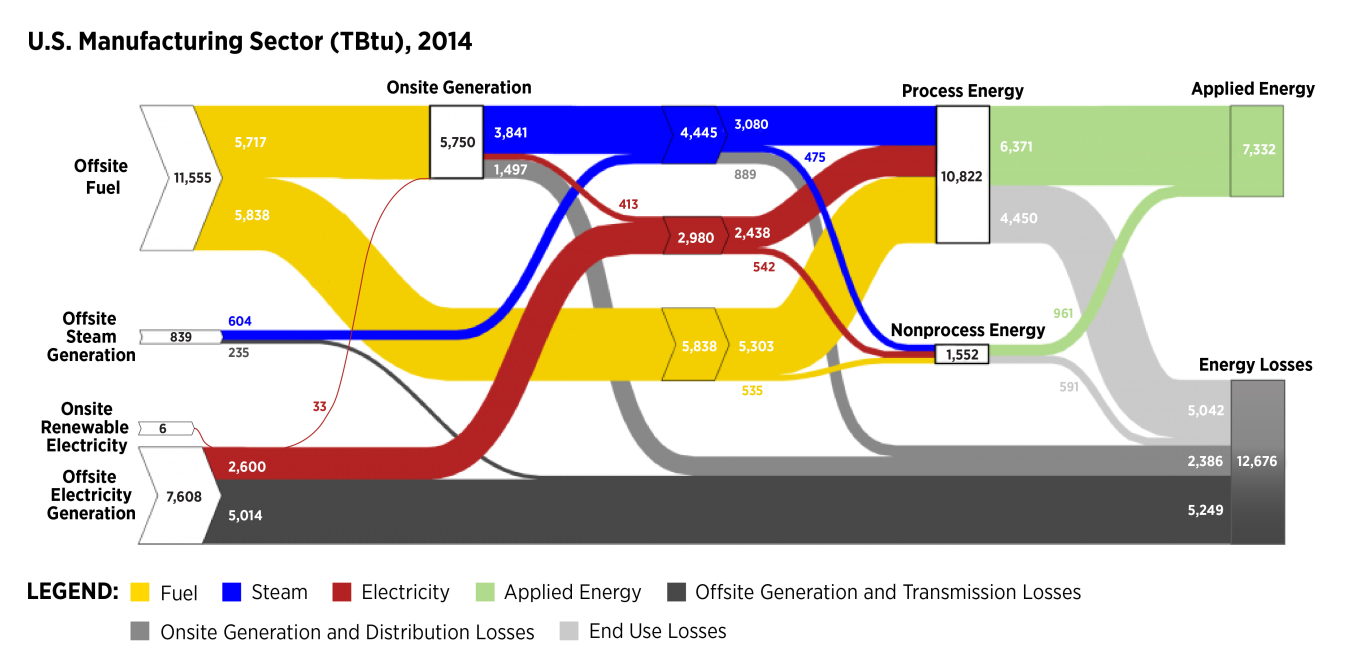
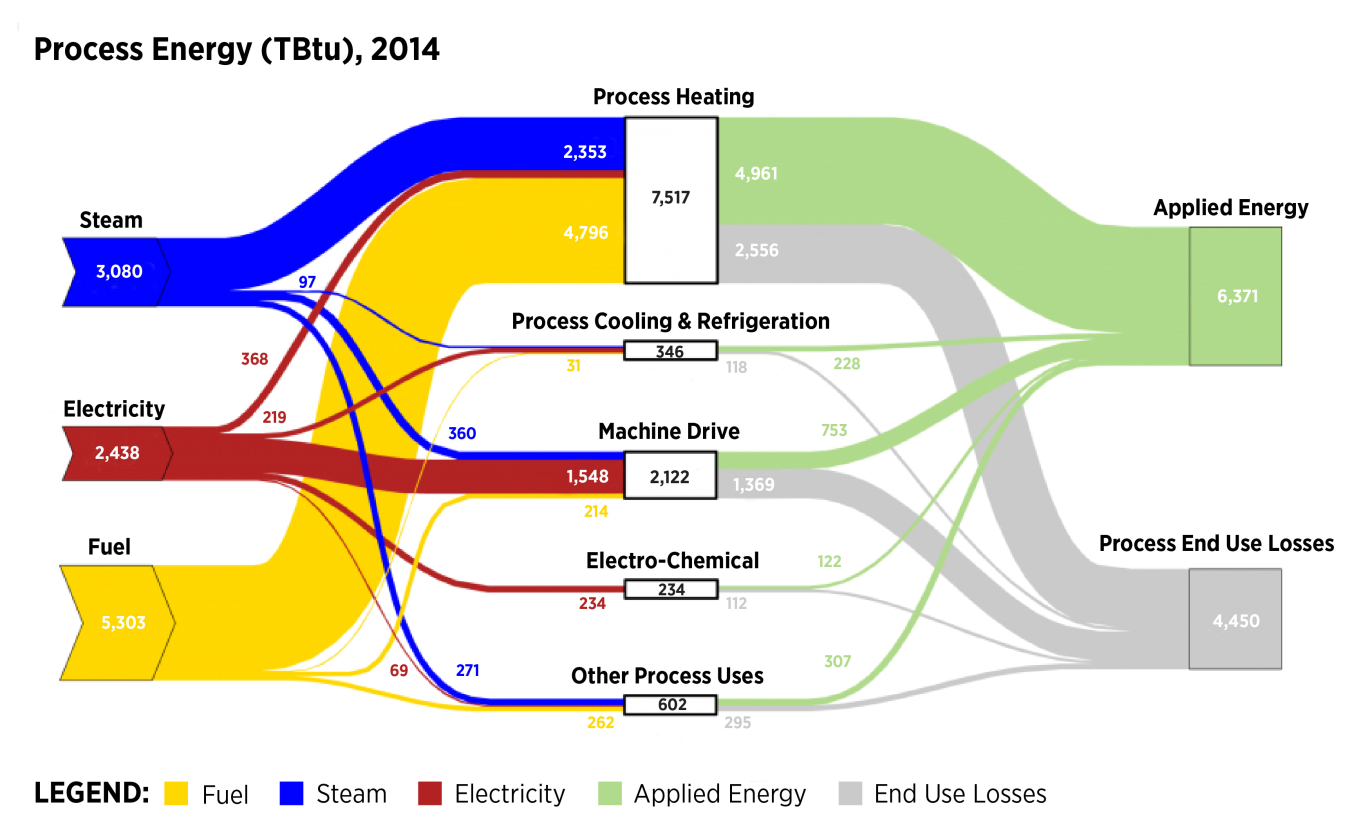
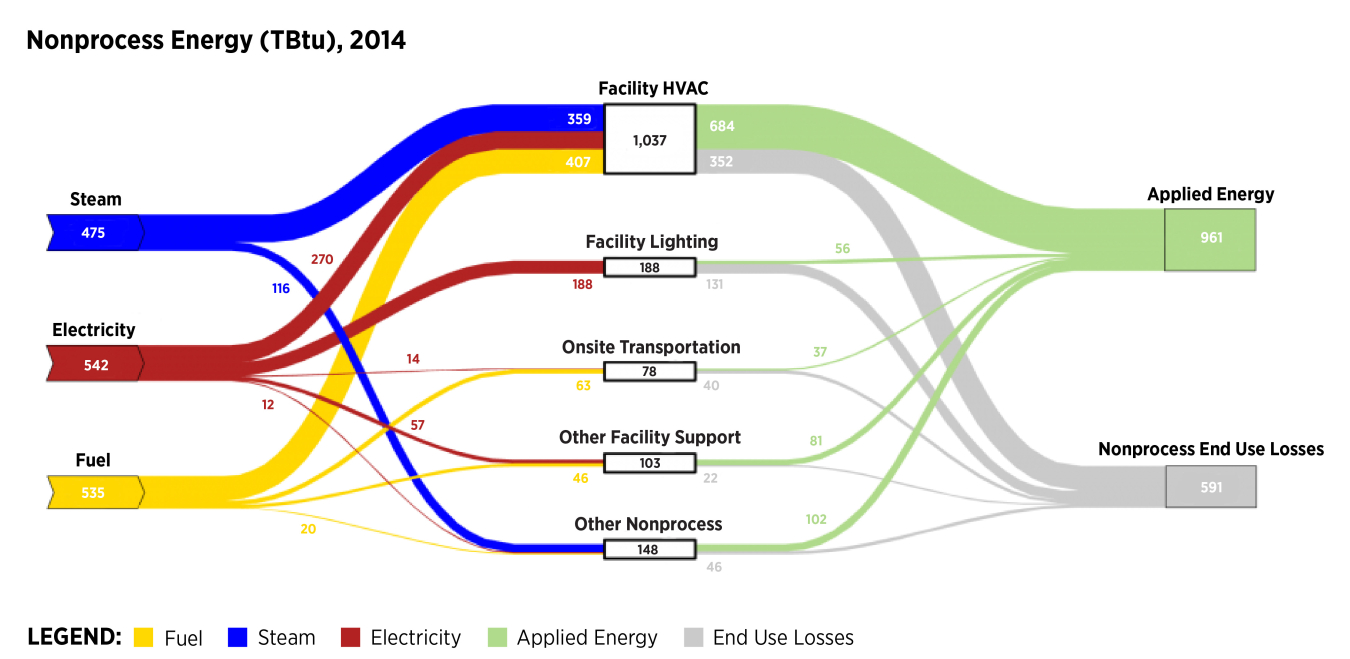
Click on the Full Sector, Process Energy, or Nonprocess Energy thumbnails below the diagram to see further detail on energy flows in manufacturing. Also, see the Dynamic Manufacturing Energy Sankey Tool to pan, zoom, and customize the manufacturing Sankey data and compare energy consumption across manufacturing subsectors (this tool is only available for 2010 MECS data).
The Onsite Generation Sankey diagram below shows offsite inputs of fuel and electricity that flow to conventional boilers, combined heat and power (CHP), and other steam- and/or electricity-generating systems. Generating steam and electricity onsite for use in plant operations results in some energy losses, which are estimated. Electricity generated from CHP systems, power systems (e.g., diesel generators), and onsite renewable energy from non-biomass sources is combined in the electricity output. Over 3,841 TBtu of steam and 413 TBtu of electricity were directly employed in end use manufacturing applications in 2014.
These diagrams visually complement the 2014 MECS Manufacturing Energy and Carbon Footprint analysis. Definitions of terms used in this Sankey diagram are at the bottom of this page.
TERMINOLOGY
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)/Cogeneration: The production of electrical energy and another form of useful energy (such as heat or steam) through the sequential use of energy.
Conventional Boilers: Boiler vessels that consume fuels or electricity as the primary energy source to produce heat that generates steam or hot water. Boiler losses represent energy lost due to boiler inefficiency.
Offsite Electricity Generation (net) (onsite generation input): The sum of purchased electricity and electricity transfers into the plant boundary and consumed in onsite generation (including electricity generated onsite from noncombustion renewable resources to align with MECS Table 5.2 values), less quantities sold and transferred out. This value does not include onsite generation from combustible fuels or onsite cogeneration which are all accounted for by the “other electricity generation” and “CHP/cogeneration” values.
Offsite Fuel: The sum of purchased fuel, fuel transferred into the plant boundary, and byproduct fuel (from externally sourced feedstocks or nonenergy inputs) produced and consumed onsite.
Onsite Generation: The generation of steam or electricity within the plant boundaries using fuel or electricity. Onsite generation includes three categories: “conventional boilers” (to produce steam), “CHP/cogeneration” (to produce steam and electricity), and “other onsite electricity generation” (defined below).
Onsite Generation Losses: Energy that is lost during the transformation of fuel into steam and electricity within the plant boundary.
Other Onsite Electricity Generation: Consists of onsite electricity obtained from generators running on combustible energy sources including natural gas, fuel oils, and coal. Amounts of electricity generated onsite from renewable sources other than biomass (e.g., solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal) are noted on the footprints, however this output is excluded from “other electricity generation” values and instead is incorporated within the offsite electricity generation (net) to align with MECS Table 5.2 values.
ACRONYM
CHP: Combined Heat and Power
NOTES
- The data source for this Sankey Diagram is the 2014 Manufacturing Energy and Carbon Footprint. The footprint analysis utilizes 2014 EIA Manufacturing Energy Consumption Survey (MECS) data, with adjustments, to quantify steam generation, electricity generation, and incoming fuel; onsite steam and electricity generation; and end use of electricity and fuel. Steam end use is not provided by MECS but rather is dependent on analysis alone.
- Energy values represent aggregate sector-wide data for 2014 in TBtu/yr, rounded to nearest whole number
- Excludes feedstock energy (byproduct fuels from feedstock are included)
- Arrow and box heights are proportional to flow size except for small flows for visual convenience
- Energy losses do not equate to recoverable energy, as a portion of these losses are thermodynamically unrecoverable
- Offsite generation shown on net basis (purchases, sales, and transfers accounted for)
- Offsite generation and transmission losses are not included in the Onsite Generation Sankey