RSS









Below are stories about next-generation technologies featured by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Wind Energy Technologies Office.
Subscribe to the WETO E-Newsletter
Subscribe to the WETO e-newsletter to stay informed on the latest wind energy news, events, publications, and updates.

Over the past decade, the wind fleet’s average capacity factor has increased substantially. Researchers have been debating how much of the improvement should be credited to technology versus increasing wind speeds.

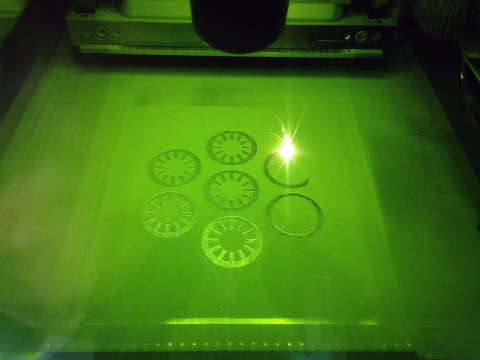
DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and National Renewable Energy Laboratory have published a study as part of the MADE3D initiative, highlighting 3D printing of magnetic components for large electrical machines like wind turbines.
The National Offshore Wind R&D Consortium has announced six new projects to support supply chain efficiency, asset monitoring, and inspection.

WETO has released phase I findings for its Big Adaptive Rotor project, studying large blades for low-specific-power wind turbines.

This report assesses the potential for, and technical viability of, airborne wind energy (AWE) in the US. Findings include data on the resource potential of wind energy available to AWE systems and what’s needed for AWE to deploy at meaningful scales.
As 2021 draws to a close, the Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO) is reflecting on our R&D, recent achievements, and recognitions, and getting ramped up for a new year of possibilities for wind energy.
Researchers from NREL and GE have developed and demonstrated the world’s first turbine that can jump-start the grid during a blackout or operate without the power grid.
DOE national labs and industry partner Vestas published a report discussing how 3-D printing may hold promise for producing specific wind energy components.

R&D World magazine has recognized three WETO-supported projects for its 2021 R&D 100 awards, which celebrate products and technologies that are considered innovative disruptors and revolutionary ideas in science and technology.

As wind turbines and plant sizes grow, is there a point at which costs plateau? Researchers analyze the avg cost per megawatt to develop and maintain offshore wind plants—and how these could change if trends toward larger turbines and plants continue.

