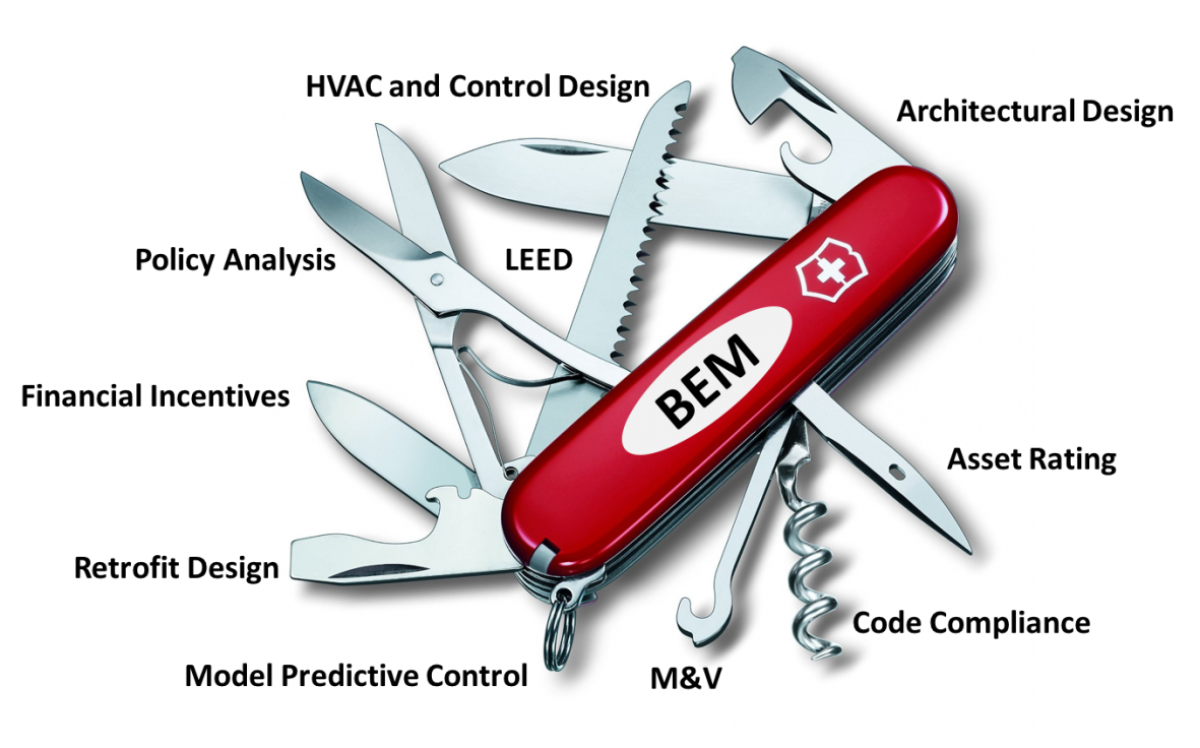



Building Energy Modeling (BEM)—physics-based software simulation of building energy use—is a multipurpose tool for building energy efficiency, supporting a variety of applications. The most traditional, and most intuitive, applications of BEM are in architectural, mechanical, and control design of new buildings and retrofits. The ability of BEM to evaluate buildings under standard weather and operating conditions—an evaluation that is impractical to perform in the physical world—is the basis of applications in code-compliance, green certification, and project documentation for financial incentives. BEM is also used to conduct large-scale analysis—at the level of a utility service territory—to inform policy decisions and to develop per-project and overall savings estimates. Emerging use cases of BEM include dynamic applications like model predictive control, where a model of a building is integrated with real-time information from weather forecasts, the building automation system, and the grid to evaluate and choose optimal short-term building control strategies.

