
Work with the DOE Labs
In 2010 alone, the Energy Department’s 17 National Laboratories and 5 facilities executed more than 13,500 technology transfer transactions. Learn more about the ways we are tapping the potential of the Energy Department's scientific discoveries.
Supercomputers: Pictorial Superpowers
From supernovae to Parkinson’s disease: computer simulations catalyzing discoveries.
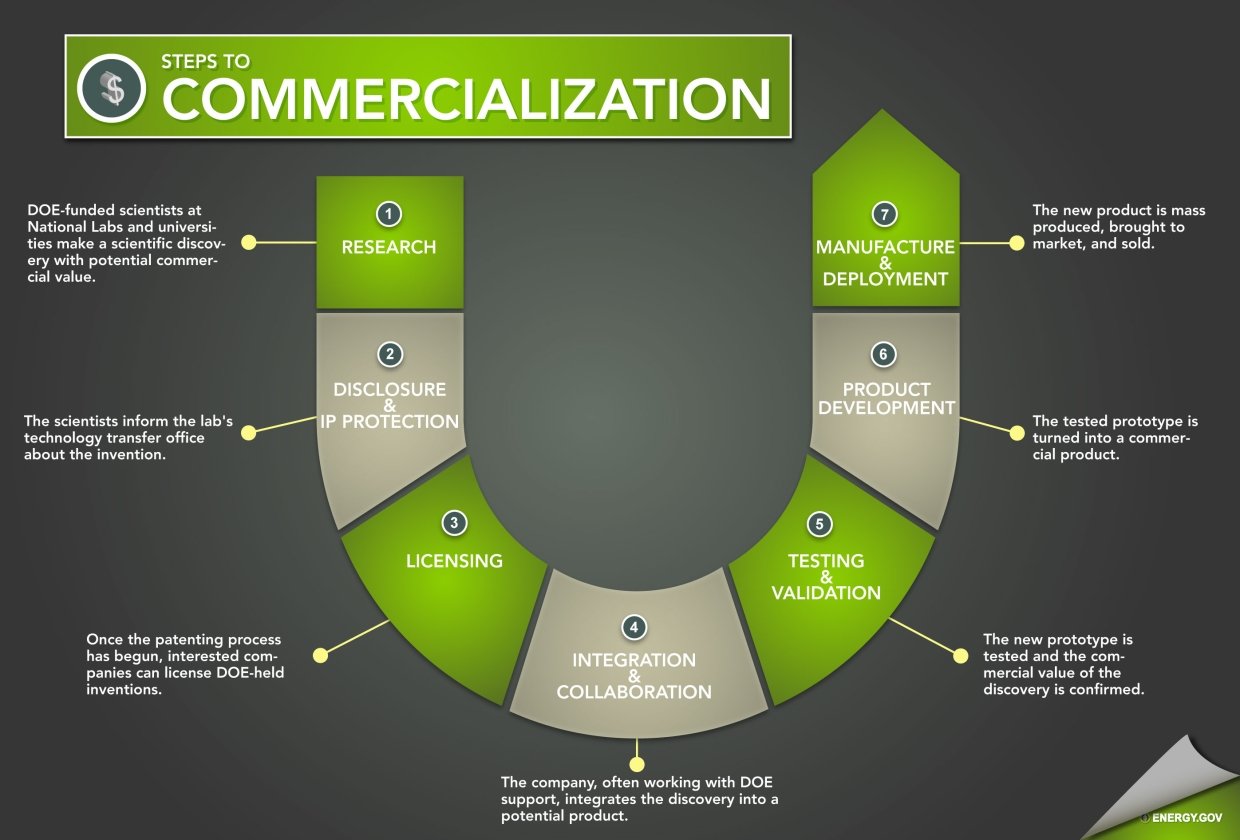
Commercialization
Learn how our National Labs and facilities are creating jobs, businesses and industries, impacting Americans' lives.
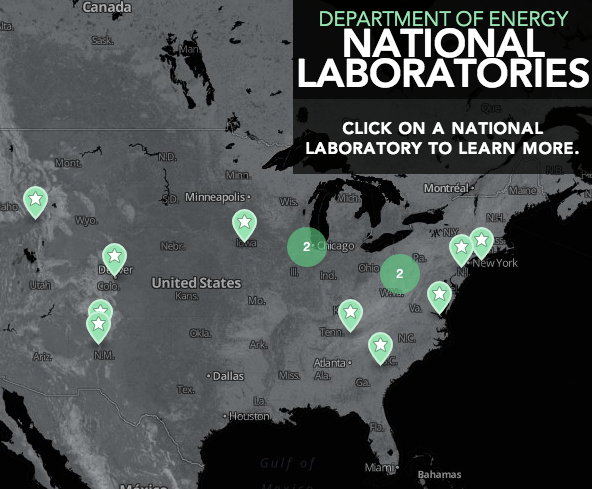
National Laboratories
Do you know where our 17 labs are located?

Energy Innovation Portal
Energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies available for licensing.
Quadrennial Technology Review
Strengthening and streamlining how the Department achieves its energy, economic and environmental goals over the next five year.

