Manufacturers have been adopting technologies that improve the efficiency of light-duty vehicles and allow them to achieve greater fuel economy.
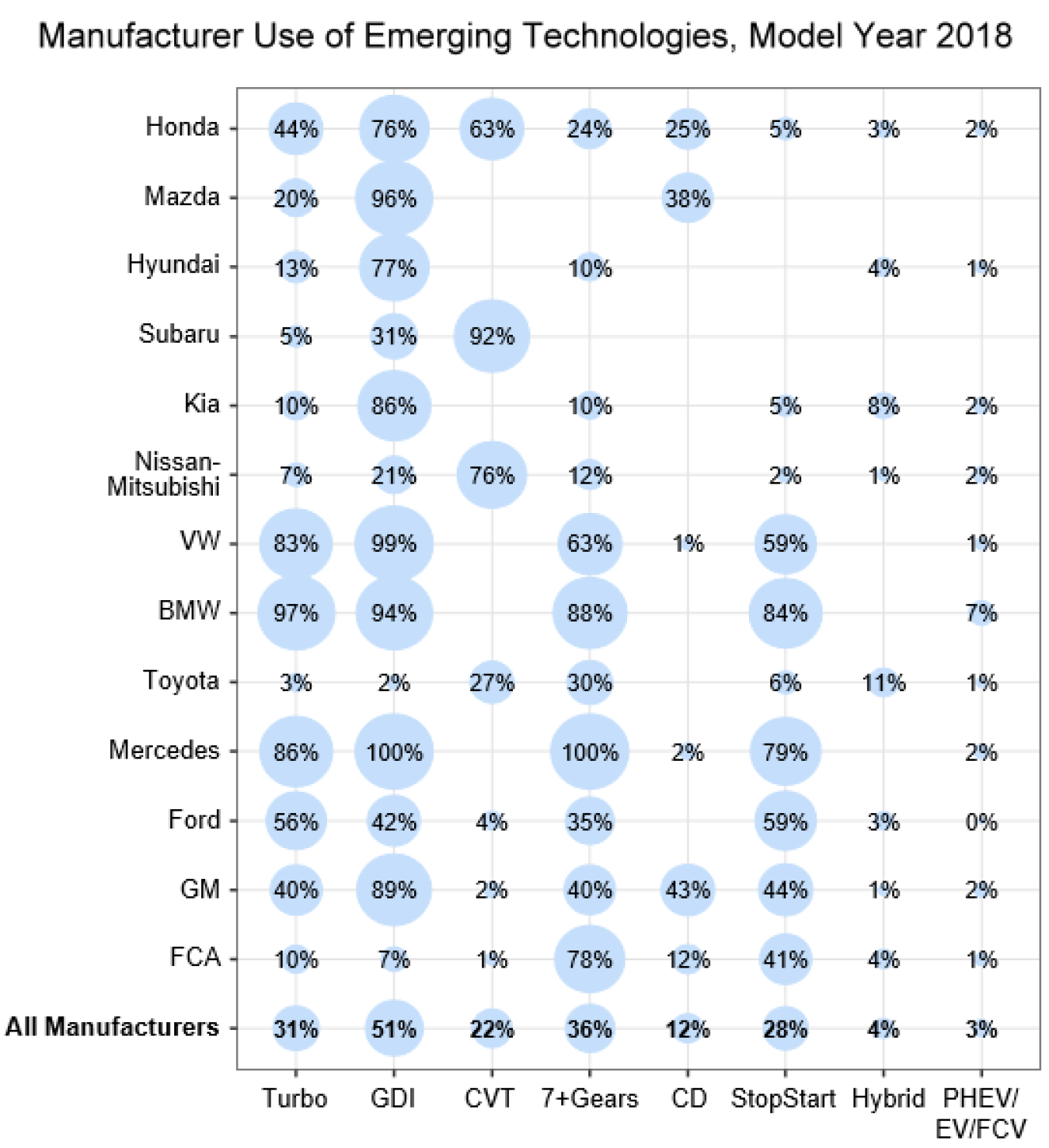
April 15, 2019Manufacturers have been adopting technologies that improve the efficiency of light-duty vehicles and allow them to achieve greater fuel economy. Of all the emerging technologies, gasoline direct injection (GDI) has seen the highest level of adoption among manufacturers, reaching 51% for the 2018 model year. Eight of the largest manufacturers installed GDI in more than 75% of the vehicles they produced, with several near or at 100%. Turbo charging and stop/start are two other engine technologies that reached a production share of about 30%, while cylinder deactivation (CD) was at 12%. Thirty-six percent of the vehicles produced had transmissions with seven or more gears while 22% were fitted with continuously variable transmissions (CVT). Gasoline hybrid vehicles accounted for 4%, while plug-in hybrid, all-electric, and fuel cell vehicles had a combined total of 3%.
Notes:
The "All Manufacturers" category includes manufacturers shown, as well as those not listed on the figure. Data for 2018 are preliminary.
GDI = Gasoline direct injection
CVT = Continuously variable transmission
CD = Cylinder deactivation
Hybrid = Gasoline hybrid that cannot be plugged in
PHEV = Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle
EV = All-electric vehicle
FCV = Fuel cell vehicle
Source: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, The 2018 EPA Automotive Trends Report: Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Fuel Economy, and Technology since 1975, EPA-420-R-19-002, March 2019.

