The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration recently published final fuel consumption standards for heavy vehicles called "vocational" vehicles. A vocational vehicle is generally a single-unit work vehicle over 8,500 lbs gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) or a passenger vehicle over 10,000 lbs GVWR that is not a combination tractor. These vehicles vary in size, and include smaller and larger van trucks, utility "bucket" trucks, tank trucks, refuse trucks, urban and over-the-road buses, fire trucks, flat-bed trucks, and dump trucks, among others. Often, these trucks are built as a chassis with an installed engine purchased from one manufacturer and an installed transmission purchased from another manufacturer. The chassis is typically then sent to a body manufacturer, which completes the vehicle by installing the appropriate feature—such as dump bed, delivery box, or utility bucket—onto the chassis. Because of the complexities associated with the wide variety of body styles, NHTSA decided to finalize a set of standards beginning in 2016 for the chassis manufacturers of vocational vehicles (but not the body builders).
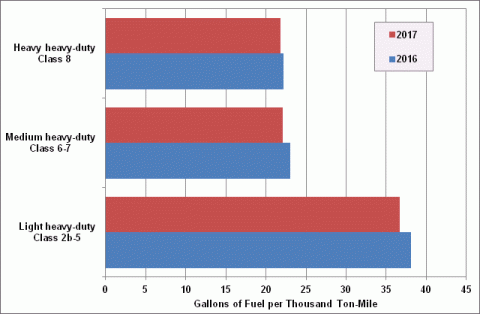
Vocational Vehicle Fuel Consumption Standards, MY 2016-2017
Note: Vehicles in classes 2b – 5 are between 8,500 and 19,500 lbs. GVWR.
Vehicles in class 6-7 are between 19,500 and 33,000 lbs. GVWR.
Vehicles in class 8 are above 33,000 lbs. GVWR.
Supporting Information
| Size Category | Truck Weight Class | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | ||
| Light heavy-duty | Class 2b-5 | 38.1 | 36.7 |
| Medium heavy-duty | Class 6-7 | 23.0 | 22.1 |
| Heavy heavy-duty | Class 8 | 22.2 | 21.8 |
Note: In addition to these standards, there were also standards set for the engines installed in vocational vehicles. | |||