Looking for an alternative to a new furnace or air conditioning system for your home, building, campus, or community?
Geothermal heating and cooling technologies are a great option.
Leer en Español
What is a Geothermal Heat Pump?
Heat pumps move heat from one place to another using electricity. Air conditioners and refrigerators are two common examples of heat pumps. Heat pumps can also be used to heat and cool buildings.
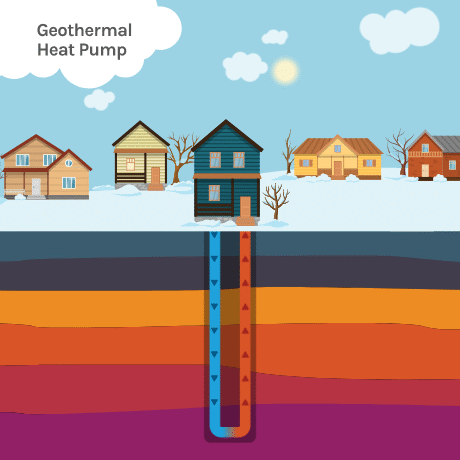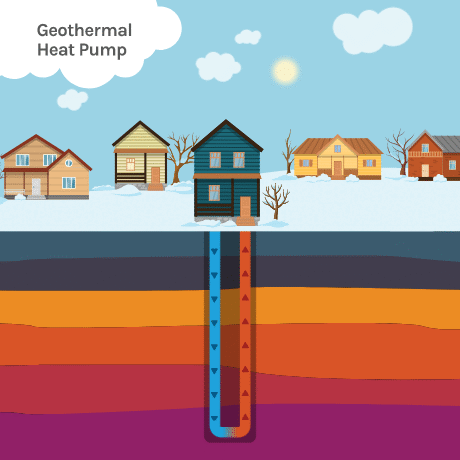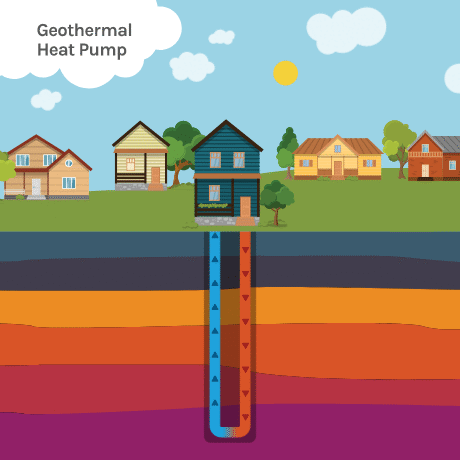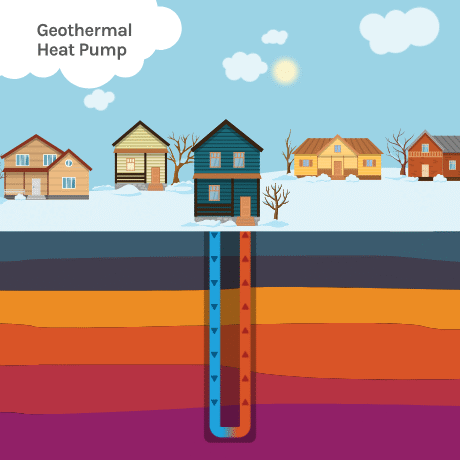
Temperatures at about 30 feet below the surface remain relatively constant year-round—between about 50°F (10°C) and 59°F (15°C). For most areas in the United States, this means soil temperatures are usually warmer than the air in winter and cooler than the air in summer.
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs), also known as ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs), take advantage of these constant underground temperatures to efficiently exchange temperatures, heating homes in the winter and cooling homes in the summer.
A GHP system includes:
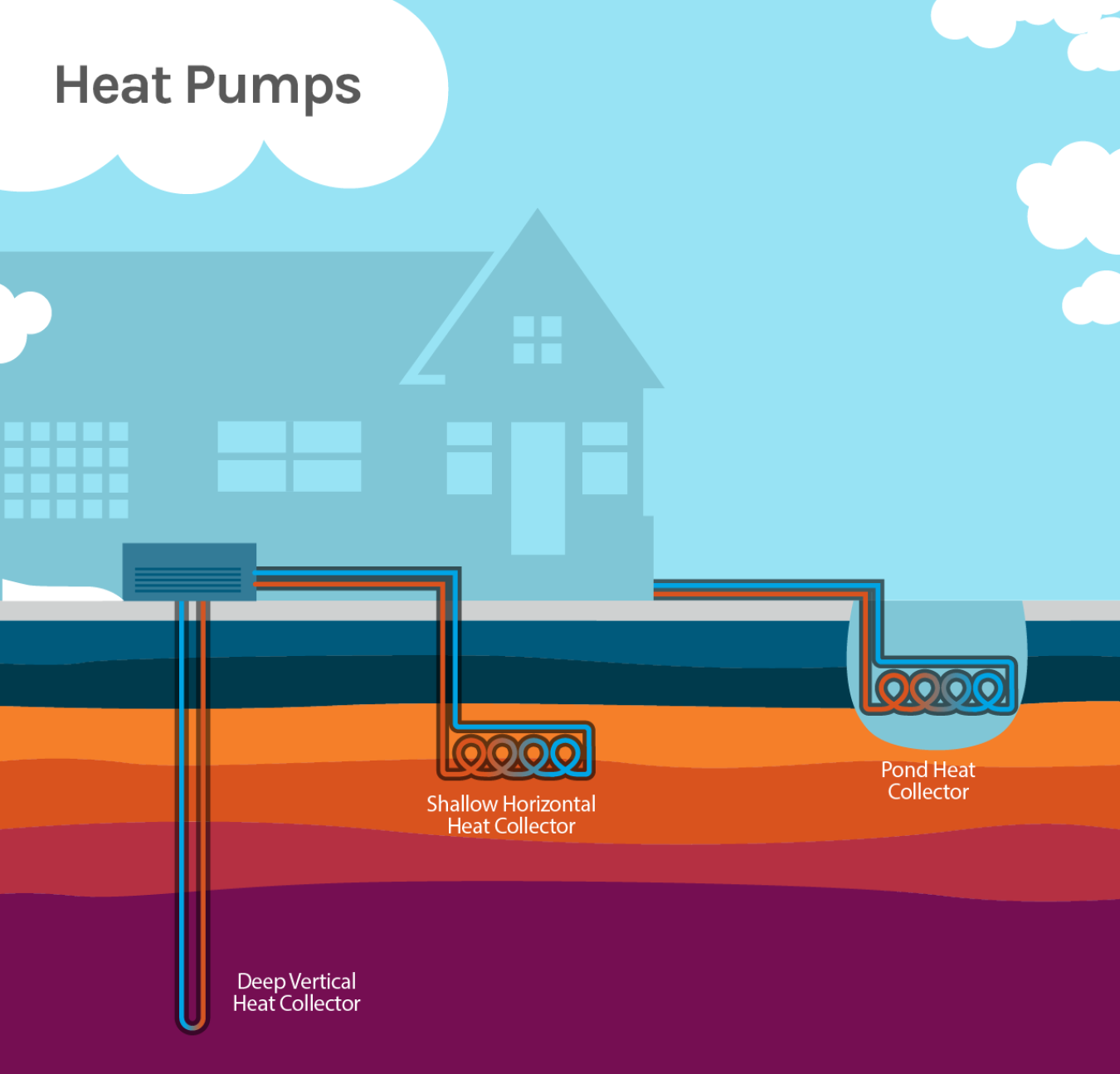
- An underground heat collector—A geothermal heat pump uses the earth as a heat source and sink (thermal storage), using a series of connected pipes buried in the ground near a building. The loop can be buried either vertically or horizontally. It circulates a fluid that absorbs or deposits heat to the surrounding soil, depending on whether the ambient (outside) air is colder or warmer than the soil.
- A heat pump—When ambient temperatures are colder than the ground, a geothermal heat pump removes heat from the collector’s fluids, concentrates it, and transfers it to the building. When ambient temperatures are warmer than the ground, the heat pump removes heat from the building and deposits it underground.
- A heat distribution subsystem—Conventional ductwork is generally used to distribute heated or cooled air from the geothermal heat pump throughout the building.
GHPs can be:
- Used to heat and cool a single house, single business, or an entire community (college campus, neighborhood, etc.)
- Implemented as part of new construction or retroactively added for existing buildings
- Installed in all climates and urban or rural environments.
Some systems can supply homes and businesses with hot water.
Read more: Types of Geothermal Heat Pumps
No, GHPs are different from air-source heat pumps. GHP systems exchange heat from the earth, while air-source heat pumps exchange heat from the air.
Compared to air-source systems, geothermal systems have been shown to be quieter, last longer, and require less maintenance, and they do not depend on the temperature of the outside air. Geothermal systems are typically more expensive than air-source systems, but the additional costs are often returned with energy savings.
Office of Geothermal Efforts to Support GHP Use
The Office of Geothermal (OG), invests in research to advance the use of geothermal heat pumps and other low temperature geothermal technologies across the country.
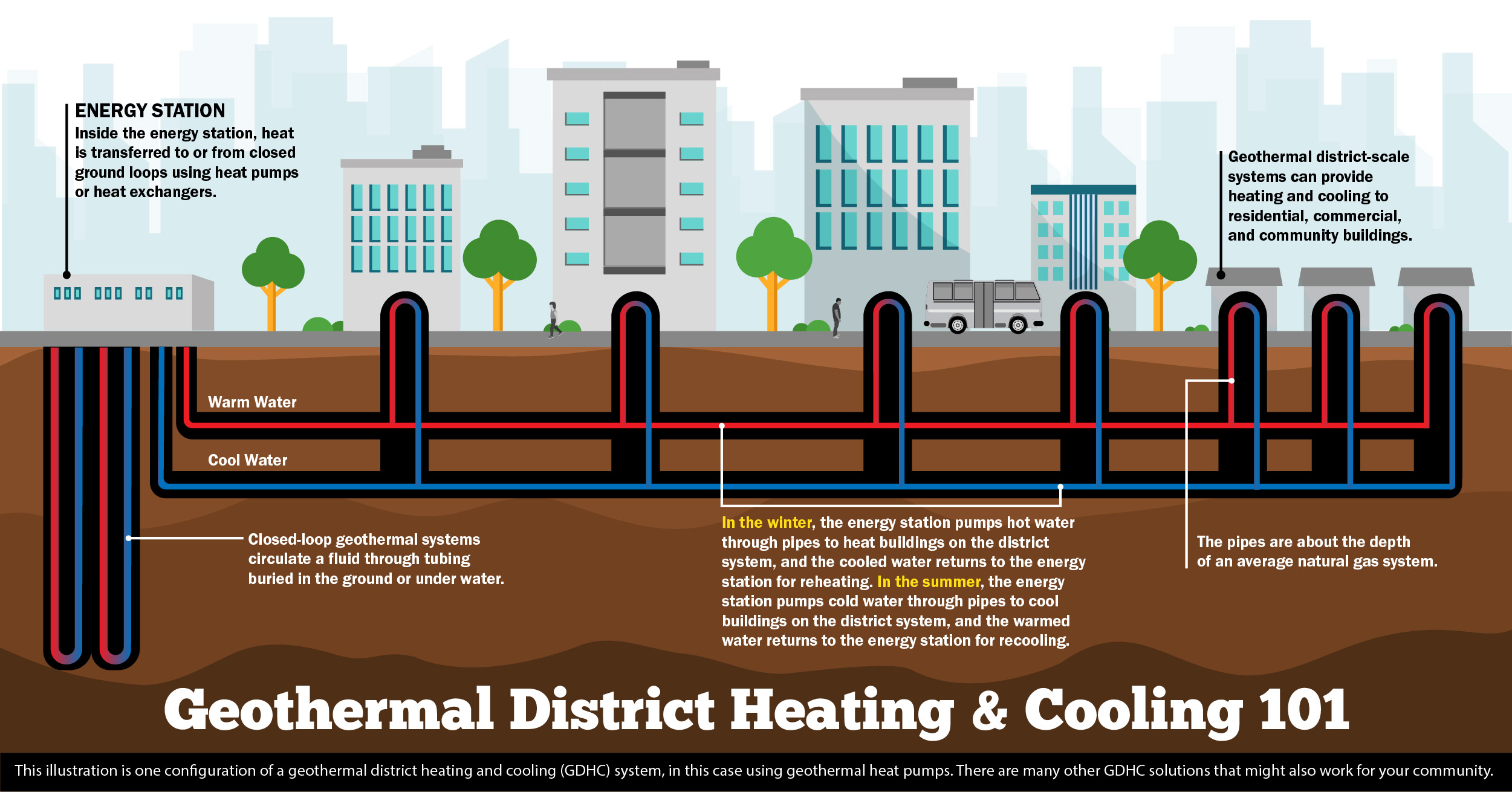
Geothermal Heating and Cooling for Communities
District and community-scale geothermal heating and cooling systems use one or more underground loops to create a heating and cooling network that can use a series of heat pumps. New and different configurations of these systems are emerging in universities and communities all over the United States.
Under the District-Scale Geothermal Energy Pilots initiative, OG is supporting three projects to install geothermal district heating and cooling systems and create related workforce training. The initiative will also help expand community-scale geothermal by supporting new systems and developing case studies to be replicated throughout the country.
Grid Impacts from Mass Deployment of Geothermal Heat Pumps
OG conducted an analysis highlighting that, deployed at mass scale and coupled with building efficiency improvements, geothermal heat pumps could bolster seasonal U.S. grid resilience, reduce electricity demands, and avoid as much as 43,500 miles of new grid transmission lines by 2050—enough to cross the continental United States eight times. Learn more by reading the report.
GHP Case Studies
OG initially released 19 case studies, since augmented with another five case studies, on GHP systems. These studies showcase installations across different U.S. climate zones, highlighting various system types, sizes, and benefits to help people better understand GHP technology. The results provide real-life examples of GHP systems in different parts of the country, making it easier for people to understand how such a system might work for them.
To explore different types of geothermal heat pumps, visit DOE’s Energy Saver page.
OG emails bring funding opportunities, events, publications, and activities directly to your inbox.