
The Baksan Experiment on Sterile Transitions (BEST) finds evidence of the sterile neutrino, a hypothetical particle that interacts only via gravity.
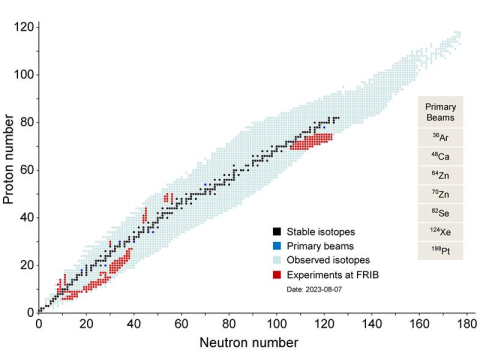
Department of Energy user facility helps probe questions from changes in the structure of nuclei to nuclear reactions that shape the Universe.
Matter inside neutron stars can have different forms: a dense liquid of nucleons or a dense liquid of quarks.
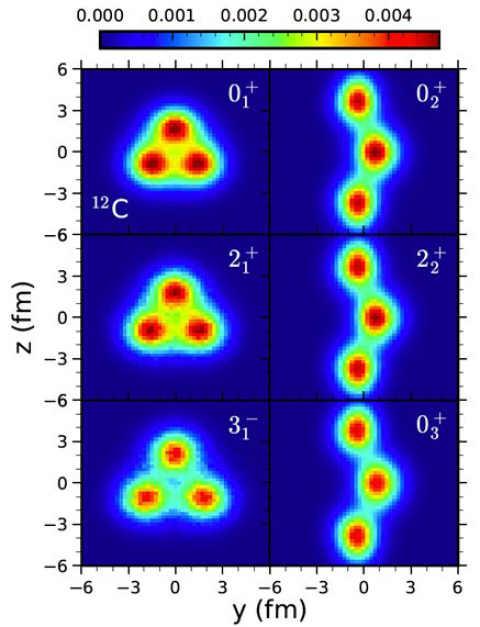
Researchers examine the structure of the low-energy nuclear states of carbon-12 using nuclear lattice effective field theory.
Scientists translate predictions of hydrodynamics into experimentally observable particle patterns.

Simulations of binary neutron star mergers suggest that future detectors will distinguish between different models of hot nuclear matter.
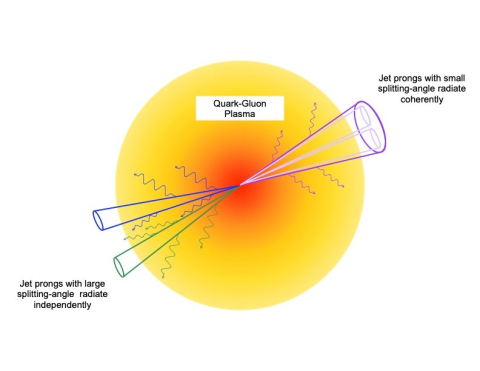
Jets of particles in quark-gluon plasma from heavy-ion collisions lose energy via radiation, but how they radiate energy depends on the jet’s structure.
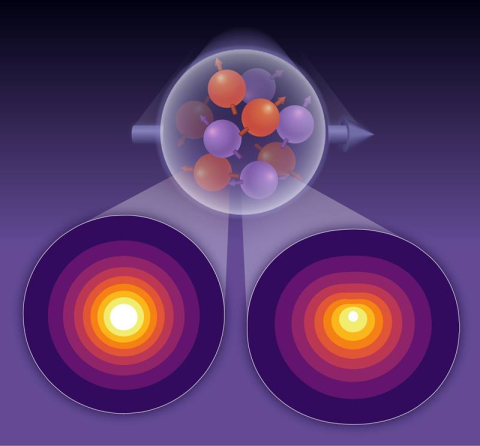
Theorists predict differential distribution of 'up' and 'down' quarks within protons—and differential contributions to the proton's properties.
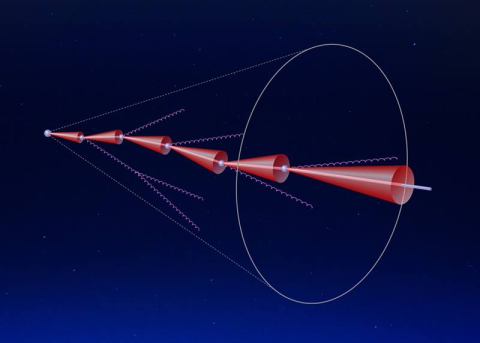
Novel techniques allow the first direct observation of a predicted effect that results in the suppression of gluon radiation emitted by a heavy quark.
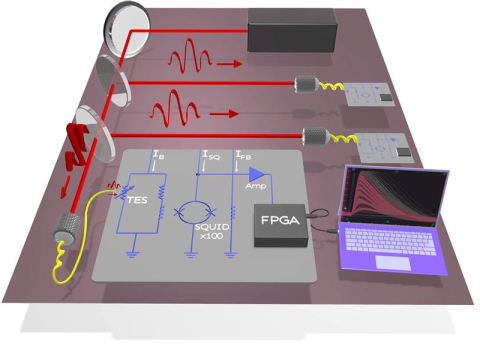
A new system for detecting photons in laser-powered quantum computers brings these systems closer to reality.

