The projects address an area vital to improving grid resilience and reliability: analysis of system performance.
November 29, 2018Each year, the R&D 100 Awards recognizes the most exceptional innovations in science and technology from the past year, as chosen by an independent panel of more than 50 judges representing R&D leaders in a variety of fields. This year’s recipients demonstrated the impressive level of innovation driving the development of important new tools and technologies at the Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Laboratories. Among the 32 awards given to DOE’s National Lab researchers were two projects supported by the Office of Electricity’s (OE) Advanced Grid R&D Division: the Dynamic Contingency Analysis Tool (DCAT) developed by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) and the Mobile Universal Grid Analyzer (m-UGA) co-developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and the University of Tennessee. Each project addresses an area of vital importance to improving the resilience and reliability of the nation’s electric grid: analysis of system performance.
Grid system operators’ and utilities’ understanding of system performance at any given moment is critical to ensure a reliable flow of electricity, undertake any necessary actions swiftly, and to recover quickly and efficiently from any disruption that may occur. While that statement is deceptively simple, analyzing performance accurately is actually quite complicated. Adding to this complexity are increasingly frequent and sophisticated cyber attacks as well as natural disasters that could impact the grid.
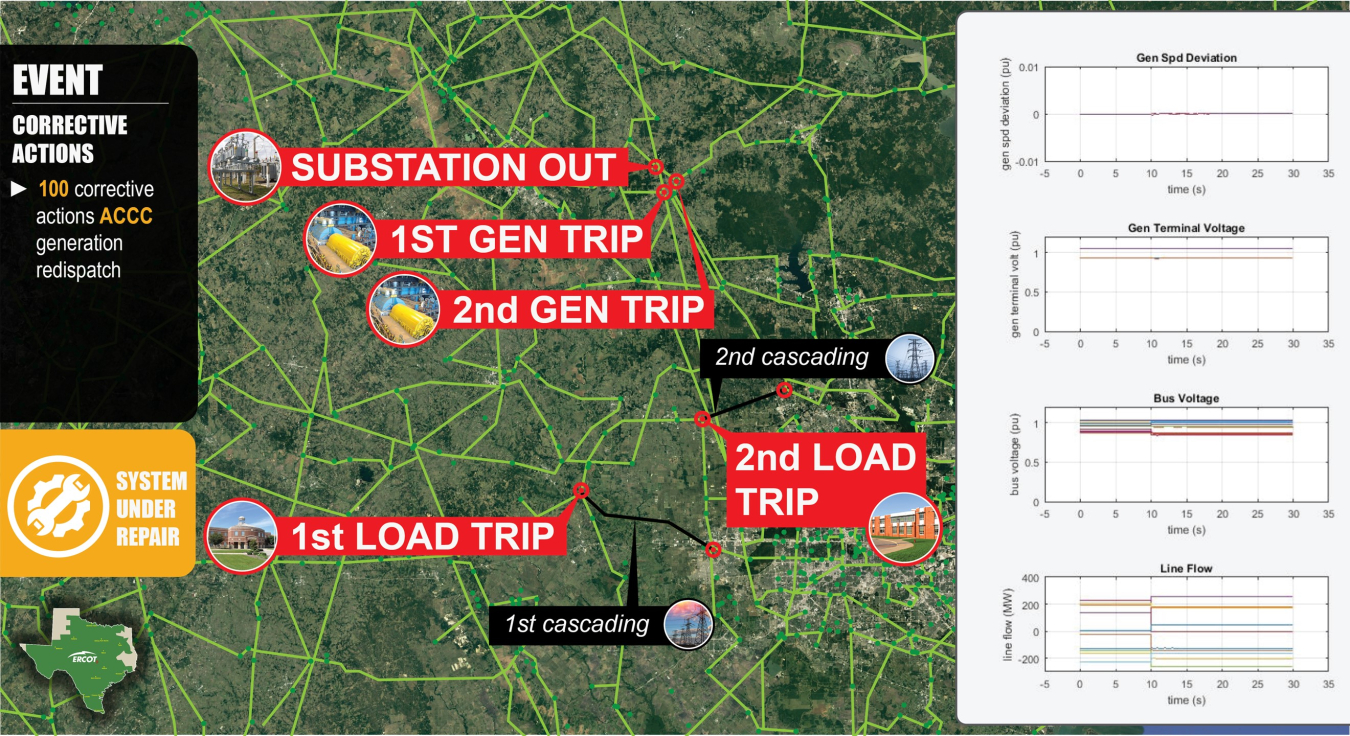
At PNNL, researchers tackled the challenge of minimizing the impact of extreme events on the power grid by building a tool that identifies weaknesses, determines the impacts that would result from a cascading power outage, and lets the power operator know what actions are needed to stop an outage before it occurs. By simulating thousands of extreme events, the DCAT automatically combines the evaluation of steady-state operations with changing occurrences in the electric grid to find weak spots. Once a weakness is identified, DCAT determines the impacts that would result from a cascading power outage and then identifies appropriate next steps. PNNL estimates using DCAT will provide utilities with gains of at least 50 percent in efficiency compared to today’s more manual processes.
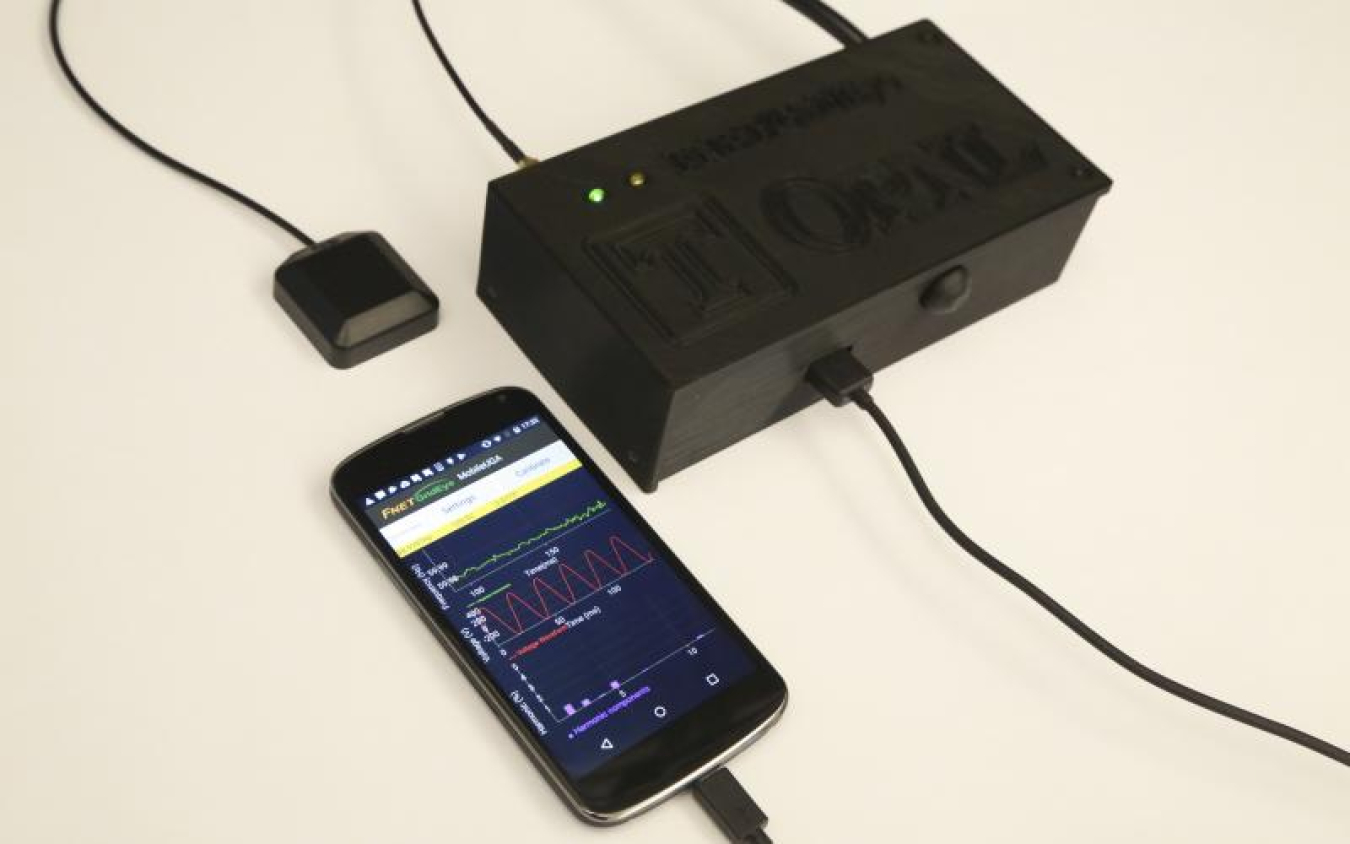
In Tennessee, ORNL and University of Tennessee researchers co-developed the m-UGA, a multi-functional wide-area monitoring and analyzing device, which enhances the situational awareness capabilities for electric power grid operators, end-users, and researchers. This means users with this time-synchronized, multi-functional, wide-area monitoring and analyzing tool can assess the health of the power grid in real time on their mobile devices. The technology can be installed virtually anywhere with regular 120V power outlets and can capture dynamic grid behaviors and monitor customer-end power quality.

OE’s vision, through a mix of technology and policy solutions conducted in partnership with the private and public sectors, is to harness innovation for a stronger, more reliable North American energy system and a path forward to energy independence. By investing in next-generation technologies and tools such as these two projects, we will continue to make progress in improving the security and resilience of the nation’s critical energy infrastructure.
Congratulations, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, on receiving these prestigious awards!
Michael Pesin, OE-10

Deputy Assistant Secretary, Grid Systems and Components
Michael Pesin is Deputy Assistant Secretary for the Grid Systems and Components Division in DOE’s Office of Electricity. His division is responsible for the development and management of projects for next-generation electricity delivery technologies and supporting activities to accelerate their introduction to the marketplace.
Mr. Pesin has over 35 years of experience in the electric utility industry directing development and execution of advanced technology programs. Mr. Pesin is a licensed professional engineer and spent most of his career leading technology organizations at electric utility companies where he led technology strategy development, managed research and development programs, and directed strategic programs and demonstration projects in generation, transmission, distribution, system protection, advanced metering infrastructure, communication networks and cybersecurity, energy storage, microgrids, electric vehicles, transactive energy, and other advanced technologies.
Prior to joining DOE, Mr. Pesin was also the founder and president of a consulting company working with electric utilities, technology companies, and investors. He served as a board member at a number of technology organizations, is actively involved with many electric power industry groups, and is a frequent speaker at industry events.


