DOE report identifies opportunities and challenges facing CHP technology within current regulatory environment of Mexico.
Office of International Affairs
September 3, 2018DOE Report finds Mexico is a Promising Market for Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems
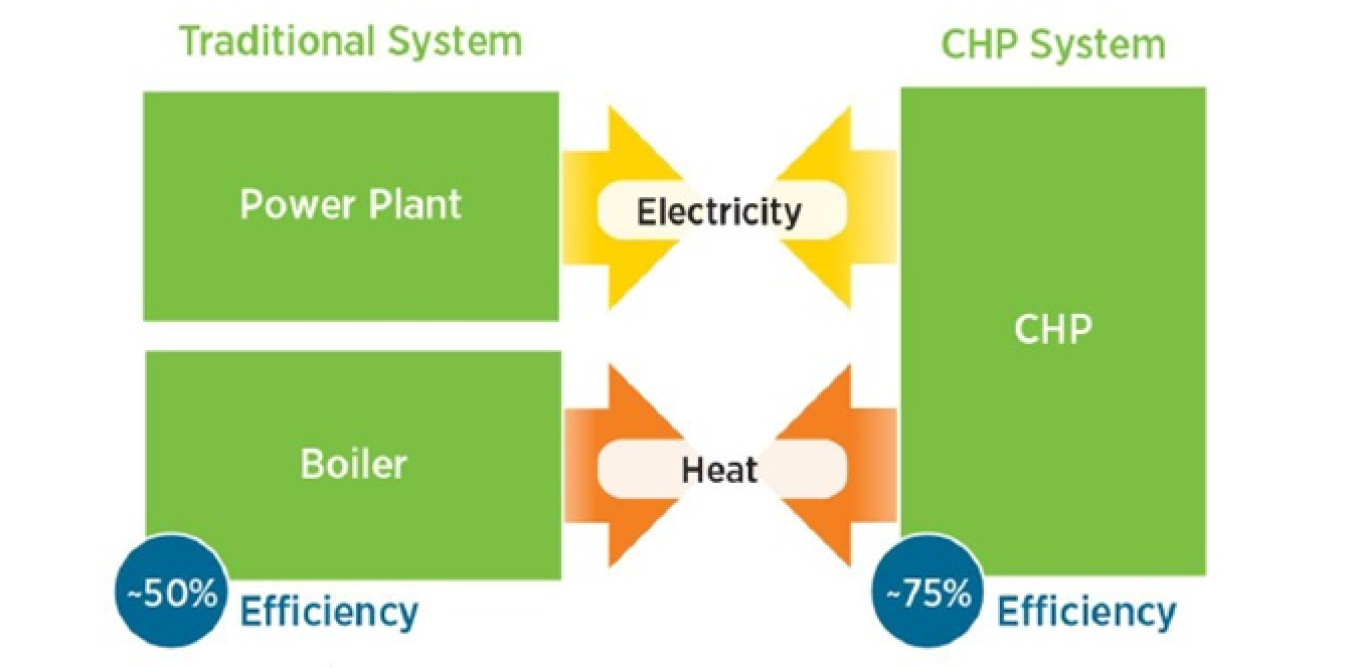
Under implementation since 2013, energy reforms in Mexico have provided new opportunities for the CHP1 industry by facilitating competition and investment in natural gas, the primary fuel source for CHP systems. The U.S. Department of Energy commissioned a report to identify opportunities and challenges facing U.S. suppliers of CHP technology and services within the context of the current energy regulatory environment in Mexico. The report, prepared by Oak Ridge National Laboratory, also provides an overview of the current energy policy environment and the electricity market dynamics related to the CHP sector in Mexico. Beyond the identification of commercial opportunities, companies interested in entering the CHP market in Mexico will find the report a valuable reference on the process for obtaining generation permits, accreditation for efficient CHP, and interconnection to the grid.
Drafted in collaboration with industry stakeholders in the United States and Mexico, the report finds a long-term promising market for CHP in Mexico and Identifies three primary trends driving it:
- Growing electricity use and peak demand needs make self-supply CHP a useful technical solution to reduce demand on the grid and increase reliability and resilience.
- Public policies supporting CHP as clean energy facilitate the adoption of CHP, since efficient CHP can earn Clean Energy Certificates.
- Energy sector reforms increase access to natural gas supply, the primary source fuel for CHP systems, including greater access to gas imports from the United States.
The report also suggests several challenges hindering the full potential adoption of CHP technologies in Mexico, including:
- Lack of information and education on a) permitting, regulations, efficient accreditation, and interconnection; and b) CHP project feasibility evaluation and assumptions.
- Market and financial barriers, especially high costs for lower power units, lack of natural gas infrastructure in many areas, volatile electricity and low natural gas prices, and lack of an open market to trade Clean Energy Certificates.
The Report and Summary Fact Sheet are now available.
| 1 Combined Heat and Power (CHP), or cogeneration is the concurrent production of electricity or mechanical power and useful thermal energy from a single energy input. CHP technologies provide manufacturing facilities, commercial and institutional buildings, and communities with ways to reduce energy costs and emissions while also providing more resilient and reliable electric power and thermal energy, therefore improving overall energy security. |

