The State and Local Planning for Energy (SLOPE) Platform is a free, easy-to-use online platform to support data-driven state and local energy and decarbonization planning. SLOPE is a collaboration between nine U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) offices and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) designed to support state and local governments and other key energy planning stakeholders in building a clean energy economy. Use SLOPE to:
- Understand the various cost-effective options that meet your clean energy and climate goals.
- Access a wealth of energy data and tools in one place.
- Explore the impacts of energy strategies through an integrated, easy-to-use platform with compelling data visualizations.
- Make data-driven decisions to propel your community's energy goals.
- Create and download customized maps, charts, and scenario models to share data with other decision makers.
How to Use SLOPE
SLOPE houses two distinct tools to support your jurisdiction's planning needs:
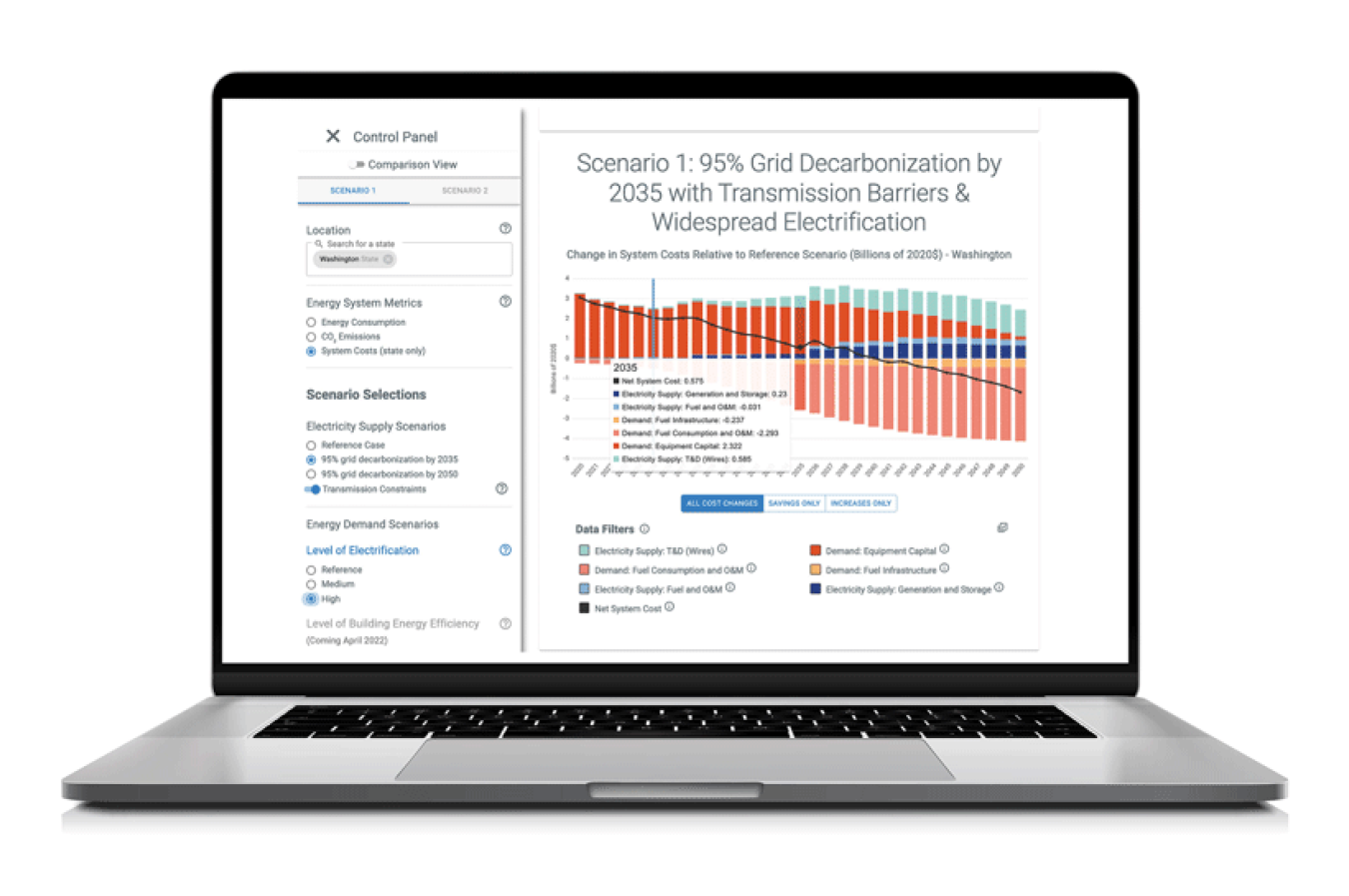
- Scenario Planner: Build, view, and compare different energy strategies and visualize scenarios for future energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and system costs for states and counties.
- Data Viewer: Explore interactive maps and charts of city, county, and state data on energy efficiency, renewable energy, and sustainable transportation.
SLOPE can help your state or local government answer questions such as:
- How can various energy strategies help my community achieve its energy or decarbonization goals?
- How do the system cost and CO2 emissions impacts of various energy strategies compare?
- How much of my community's energy consumption can be met by locally generated renewable energy?
- What portion of my state's electricity might be generated by renewable energy in the future under different scenarios?
- How much can my jurisdiction reduce energy consumption in the residential sector, and which efficiency measures have the greatest impact?
- How many commercial buildings over 20,000 ft2 are in my city, and what is the total square footage broken down by property type?
- How do energy costs and generation potential compare across technologies, jurisdictions, and regions?
- How might electric vehicle adoption change my community's electricity demand over time?
SLOPE Data at a Glance
DOE and NREL launched SLOPE in December 2019 and continue to add new data and functionality to enhance its value and improve usability. As of 2022, SLOPE includes the following data.
Scenario Planner
| Planning Metrics | Energy Consumption | CO2 Emissions | System Costs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Resolution |
State and county |
State and county | State |
| Scenario Settings |
Energy Demand:
|
||
| Not Applicable |
Electricity Supply:
|
||
Data Viewer
|
Data Category |
Data Type |
Data Resolution |
|---|---|---|
|
Energy Consumption |
Electricity and Natural Gas Consumption and Expenditures: projected in a business-as-usual case for the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors through 2050. |
State, county, and city |
|
Transportation: on-road vehicle fuel consumption, vehicle miles traveled, and vehicle stock by fuel type projected under different scenarios through 2050. |
State and county |
|
|
Energy Efficiency |
Energy Efficiency Potential: electricity savings potential for residential, commercial, and industrial sectors through 2035. |
State |
|
Single-Family Home Energy Efficiency Potential: electricity and fuel savings potential from cost-effective single-family home energy improvements. |
State |
|
|
Commercial Energy Efficiency Potential: electricity and fuel savings potential from cost-effective commercial energy improvements. |
State |
|
|
Energy Generation |
Generation Potential for Renewable Technologies (at the state, county, and location-specific level outlined below): |
|
|
State |
|
|
County |
|
|
Hydraulic Watershed Boundaries and Point Location |
|
|
Generation Scenarios: projected electricity generation from various technologies through 2050 under 12 scenarios. |
State |
|
|
Cost of Energy |
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE): projected electricity costs for 16 generation technologies plus battery storage through 2050. |
State and county |
|
Levelized Cost of Saved Energy: levelized program administrator costs for electricity efficiency programs implemented from 2009–2015. |
State |
|
|
Energy and Environmental Justice |
Energy Burden: percentage of household income spent on housing energy costs and transportation energy costs. |
Census, county, and state |
|
Energy Efficiency Bill Savings Potential for Low-to-Moderate Income Households: average energy bill savings for a cost-effective package of energy efficiency upgrades. |
County and state |
|
|
Social Vulnerability: classification of vulnerability based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Social Vulnerability Index. |
Census, county, and state |
|
|
Demographics |
Population: past and projected population from 2015–2050. |
State, county, and city |
|
Commercial Buildings |
Building Count and Area: commercial building count and area by size and property type for 2020. |
State, county, and city |
Tables 1 & 2. For a list of SLOPE's data sources, please see SLOPE FAQs—"What Are SLOPE's Data Sources?"
Additional Resources
About SLOPE
Webinars
- Introducing SLOPE's New Scenario Planner Tool (focused on the Scenario Planner)
- Visualize Your Energy Future with SLOPE (focused on the Data Viewer)
- Leveling the SLOPE: Helping State and Local Governments Reach Their Energy Goals (focused on the Data Viewer).
SLOPE Stories
SLOPE Background
As more state and local governments develop comprehensive energy plans, the adoption of clean energy technologies has become a focal point of many planning processes. Although extensive resources and data exist to help states, counties, and cities identify opportunities to deploy these technologies, the dispersed, unintegrated, and sometimes inaccessible nature of this data makes it difficult for state and local governments to easily consider, compare, or fully capture the value of this information.
To ensure SLOPE meets stakeholder needs and fills gaps in existing tools and resources, DOE and NREL gathered input on energy planning priorities and data needs from a geographically diverse group of more than 50 state and local governments and other key stakeholders and reviewed the landscape of existing energy planning tools and resources. This research demonstrated that a wide array of data, reports, and tools are available to support state and local energy planning; however, data collection at the sub-state level remains particularly burdensome. Stakeholders struggle to choose between available tools and face obstacles in the level of training and investment required to obtain useful data and outputs.
SLOPE is designed to provide these stakeholders with an accessible platform with outputs that are easily conveyed to decision makers. The platform addresses stakeholder needs such as access to localized data, interoperability between tools, and integration of data across sectors and technologies to illustrate opportunities for achieving goals and understanding the impacts of energy actions. To clearly communicate this information, SLOPE presents data in multiple formats, including maps, time series charts, and scenario models.
Contact Us
Questions or comments about SLOPE? Please contact slope@nrel.gov to share any questions or feedback with DOE and NREL.