Using funds from the U.S. Department of Energy State Energy Program (SEP), Minnesota pursued inclusive electrification strategies through an extensive stakeholder engagement project.
Giving All Communities a Seat at the Table
Electrification is critical for reducing carbon emissions and fighting climate change, but it entails substantial changes that bring benefits, concerns, and challenges for communities. Between 2020 and 2022, the Minnesota Department of Commerce, Division of Energy Resources (DOC-DER) spearheaded a stakeholder engagement project to make sure that all communities have a seat at the table while forming solutions to fight climate change.
Through this project, Minnesota fostered discussions around different interests and priorities relating to electrifications to best inform meaningful and inclusive electrification legislation. SEP awarded competitive funding to support this project, which serves as a model to other states that also want to ensure extensive stakeholder engagement plays a role in their electrification programs.
What is Electrification?
Electrification, which refers to the process of replacing technologies that use fossil fuels as a source of energy with those that use electricity, continues to be a vital tool in mitigating climate change and has the potential to generate a range of environmental, economic, and social benefits.
In 2018, DOC-DER collected feedback from Minnesota stakeholders including utilities, advocates, and trade groups, finding that stakeholders saw a significant role for electrification in reducing carbon emissions and modernizing the grid. DOC-DER saw the opportunity to further educate and learn strategies to advance electrification effectively and equitably from a broader range of stakeholders. That same year, a project team at DOC-DER received a competitive award from SEP to examine the possible benefits and concerns of using electrification as a tool for energy efficiency, carbon emissions reduction, and grid optimization in Minnesota.
Stakeholder Engagement Project
The project team launched a stakeholder engagement project in early 2020 that received strong interest and participation. More than 350 stakeholders participated in 15 meetings, contributing over 500 meeting hours and engaging with content from 37 different expert presenters.
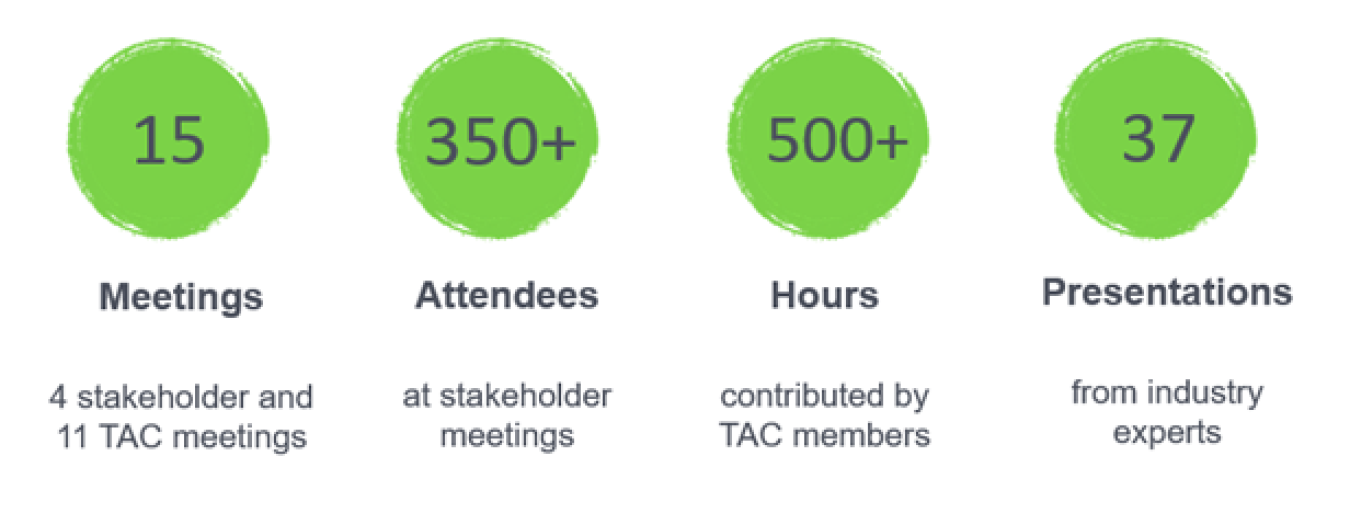
The project included a wide range of stakeholders, such as utilities, energy efficiency organizations, tribal nation representatives, advocates for low-income communities, climate advocacy organizations, organizations representing multifamily housing occupants and renters, and more. Stakeholders noted equity as a vital piece in the future of electrification to ensure that different communities have a level playing field with cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
From the first public event, I found it significant that stakeholders raised concerns about equity in the context of future electrification investments. That became a core element of this stakeholder process: How can we proactively address equity in our planning and implementation, so that we don’t continue to perpetuate a status quo that doesn’t work for every Minnesotan.”
Technical Advisory Committee
In addition to a track of open meetings focused on education among general stakeholders, the workplan included a technical advisory committee (TAC) track that convened a small group of stakeholders with energy industry expertise to focus on details of electrification metrics, grid impacts, and technologies.
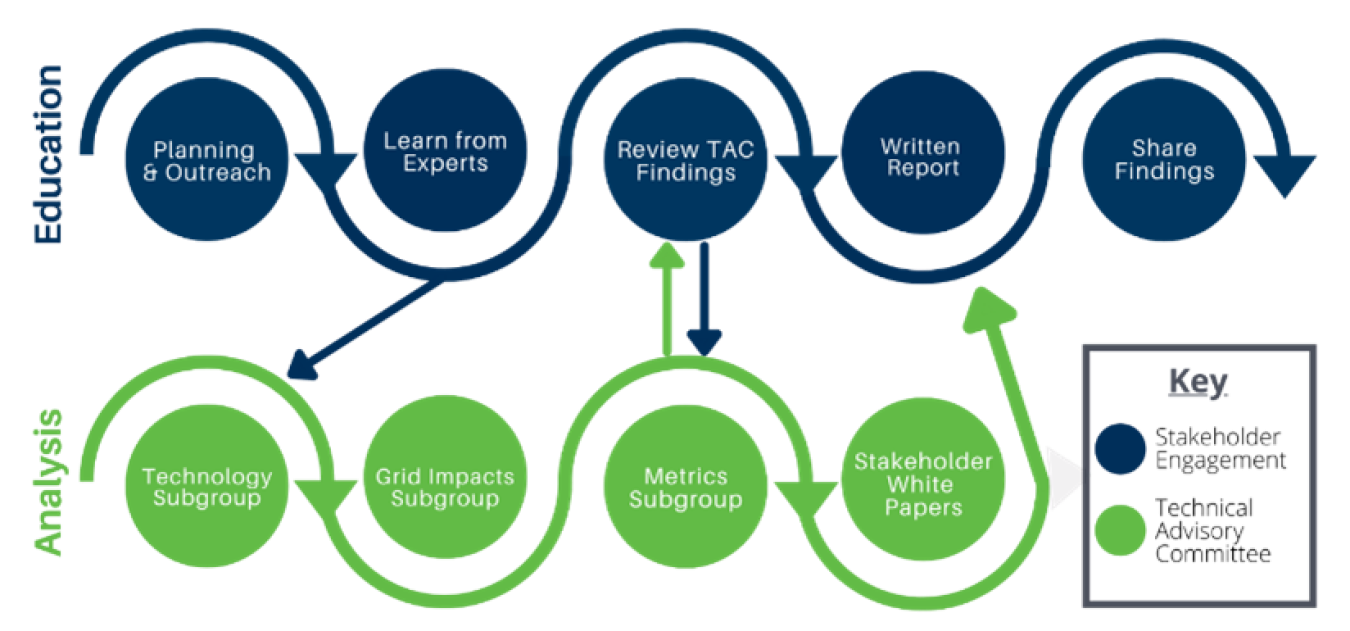
These two tracks culminated in a final report authored by DOC-DER documenting recommendations from the TACs, insights from expert presentations, and considerations for future planning efforts.
This report also includes a roadmap for other states to design and implement their own stakeholder engagement process. To complement the report, DOC-DER commissioned four white papers exploring topics and community interests that were not adequately represented during the stakeholder dialogue.
Impact of the Energy Conservation and Optimization Act
In 2021, as the stakeholder engagement project neared its end, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz signed the Energy Conservation and Optimization Act (ECO Act), which enables electrification within the state’s Conservation Improvement Program (CIP). CIP requires Minnesota electric and natural gas utilities to implement energy efficiency programs, helping residents, utilities, and businesses save money and energy, primarily through financial incentives and rebates.
The ECO Act modernized this long-standing and successful program by reversing a 16-year prohibition on promoting or incentivizing fuel switching, which includes electrification measures, with CIP funds. This development enabled the work of the DOC-DER’s stakeholder engagement project to find immediate impact as the Department of Commerce worked to develop technical guidance for utilities and other stakeholders regarding the implementation of the ECO Act.
The ECO Act identifies criteria that “efficient fuel-switching” measures and technologies must meet to be eligible within CIP, which ensure that electrification measures are cost-effective, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and source energy use, and improve the utility’s system load factor.
Stakeholder contributions during this planning period significantly helped the development of technical guidance for DOC-DER, utility, and stakeholder staff regarding how to meet those criteria and gave utility stakeholders a start in planning and developing their own ideas on how to integrate electrification into their programs. As a result, Minnesota should soon be ready to implement impactful electrification programs that advance equity and affordability.
During the course of this project, we became more educated in electrification issues – about the topics, each other’s interests and perspectives, and some of the key opportunities and challenges for the future. This nuance and understanding will serve us well as we work together implementing the ECO act.
Advancing Equitable Electrification Pathways Across the Country
By virtue of this stakeholder engagement work and the passage of the ECO Act, Minnesota is poised to become a leader in integrating electrification into its energy efficiency programs. DOE looks forward to continuing its partnerships with and support for Minnesota and other states as they explore equitable electrification pathways to design and implement electrification initiatives.
DOE’s State Energy Program provides funding and technical assistance to all 50 states, five U.S. territories, and the District of Columbia to enhance energy security, advance state-led energy initiatives, and increase energy affordability. The State Energy Program emphasizes the state’s role as the decision maker and administrator for program activities within the state that are tailored to their unique resources, delivery capacity, and energy goals.
